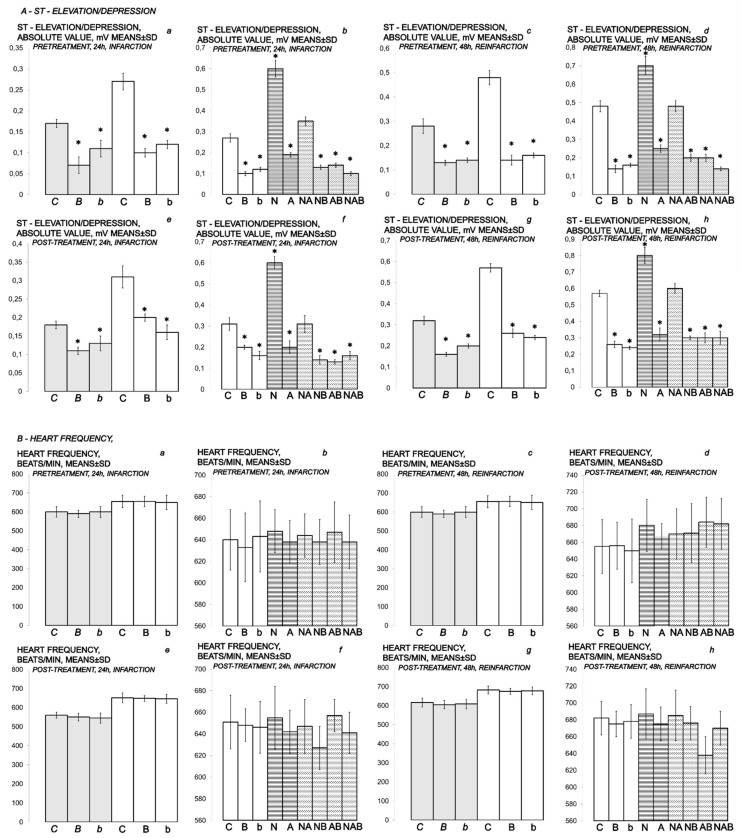
Figure 16.
(A,B) Myocardial infarction (one isoprenaline challenge) and re-infarction (two isoprenaline subsequent challenges) in isoprenaline-treated rats (75 mg/kg sc (gray bars), 150 mg/kg sc (white bars)). Gross heart lesions presentation; A–ST-ELEVATION/DEPRESSION (mV), B–HEART FREQUENCY (beats/min). Rats treated with the smaller dose of isoprenaline, 75 mg/kg sc (gray bars, italic letters), received medication (BPC 157 (10 ng/kg (b), 10 µg/kg (B) i.p. or saline (5 mL/kg i.p. (C)). Rats treated with the higher dose of isoprenaline, 150 mg/kg sc (white bars, normal letters), received medication (BPC 157 (10 ng/kg (b), 10 µg/kg (B) i.p. or saline (5 mL/kg i.p. (C)) or L-NAME (5 mg/kg i.p. (N)), L-arginine (200 mg/kg i.p. (A)) (horizontal line bars) or these agents in combination (L-NAME + L-arginine (NA), L-NAME + BPC 157 (NB), L-arginine + BPC 157 (AB), L-NAME + L-arginine + BPC 157 (NAB)) (dashed horizontal lines bars). Therapy was given (i) 30 min before isoprenaline (PRETREATMENT, prophylactic regimen (a–d)), or, alternatively, (ii) at 5 min after isoprenaline (75 mg/kg s.c. or 150 mg/kg s.c.), at day 1 and at day 2 (POST-TREATMENT, therapeutic regimen (e–h)). Ten rats per each experimental group. * p < 0.05 vs. control, at least.