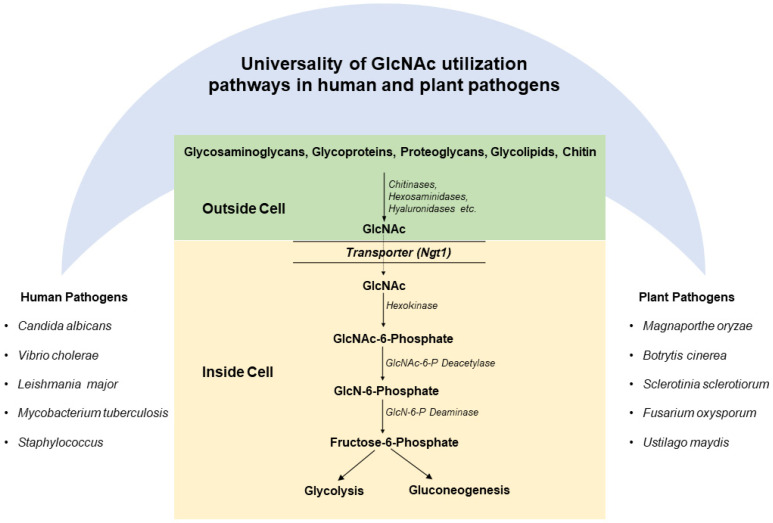
Figure 3.
GlcNAc catabolic pathway: glycosaminoglycans, glycoproteins, proteoglycans, glycolipids, and chitin are the major sources of GlcNAc. Enzymes such as chitinases, hexosaminidases, hyaluronidases, etc., release free-GlcNAc from these macromolecules, which are taken up by the pathogens. The GlcNAc catabolic pathway involves three enzymes: hexokinase, GlcNAc-6-P deacetylase, and GlcNAc-6-P deaminase, which act sequentially to convert GlcNAc into fructose-6-phosphate.