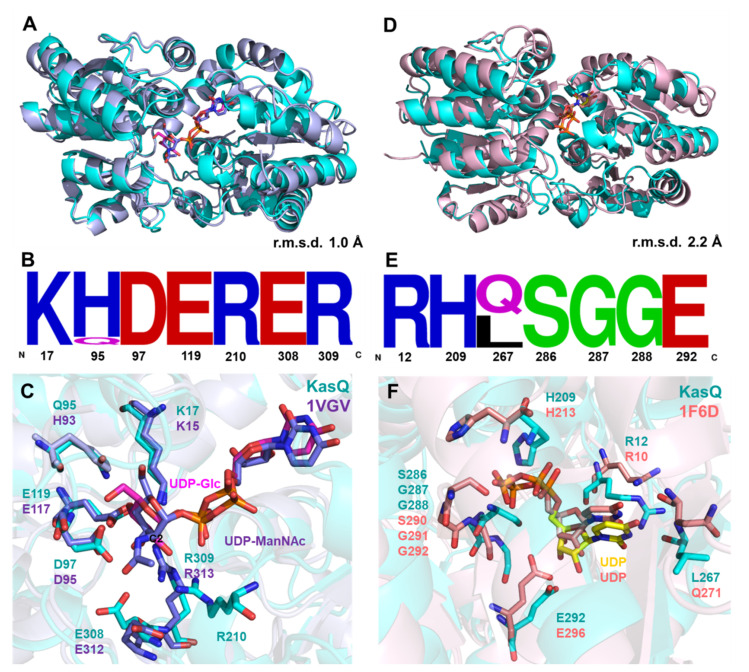
Figure 7.
Sequence and structural comparison of KasQ with reported UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerases. (A) Superimposition of KasQ–UDP-Glc monomer (cyan) with UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerases of E. coli bound with UDP-ManNAc colored blue (PDB entry 1vgv, crystal structure modeled with UDP-ManNAc, mistakenly named UDP-GlcNAc) gives an RMSD of 1.0 Å. UDP-Glc and UDP-GlcNAc are colored as pink and blue sticks, respectively. (B) Sequence logo of sugar binding-site residues amid KasQ homologs. (C) The active site of KasQ–UDP-Glc superimposed with that of E. coli bound with UDP-ManNAc. (D) Superimposition of the KasQ–UDP monomer (cyan) with the E. coli counterpart bound with UDP (PDB entry 16fd) gives an RMSD of 2.2 Å. (E) Sequence logo of UDP binding sites amid KasQ homologs. (F) Active sites of KasQ–UDP superimposed with the E. coli counterpart bound with UDP.