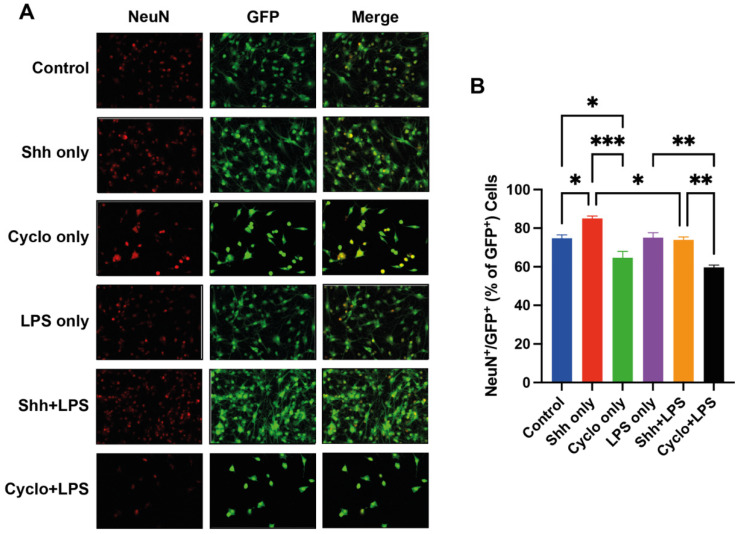
Figure 5.
Assessment of the neuronal NPC-differentiation rate by quantification of NeuN+/GFP+ cells. (A) Immunofluorescence staining for NeuN (red), GFP+ (green) NPCs, as well as NeuN+/GFP+ NPC-derived neurons. (B) The rate of neuronal NPC-differentiation (NeuN+/GFP+ cells per GFP+ cells) is significantly increased by stimulation of the Shh-pathway under normal growing conditions (Control vs. Shh only; p = 0.0370) and significantly decreased by blockage of the Shh-pathway under both, standard (Control vs. Cyclo only; p = 0.04) and inflammatory (LPS only vs. Cyclo+LPS; p = 0.001) growing conditions. Of note, the pro-neuronal differentiative effect of Shh seems to be decreased under influence of LPS (Shh only vs. Shh+LPS; p = 0.0224) Experiments performed in triplicate (n = 3), data presented as mean ± SEM, one-way-ANOVAs with post hoc Tukey-HSD tests performed for statistical analysis (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001).