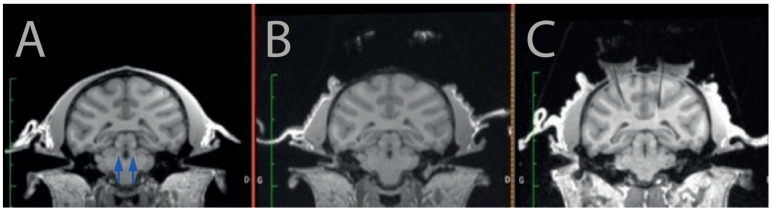
Figure 1.
Targeting the LC with MRI. The monkey was first scanned before surgery (A) to identify potential trajectories toward the LC (arrows) and to reach it from the surface of the skull without piercing a ventricle or a blood vessel. After the recording cylinders and headpost were implanted surgically, we marked a stereotaxic grid with iodin and scanned the monkey with the grid in place (B). After the grid hole that would enable to reach the LC was identified on this second scanner, we scanned the monkey a third time with an electrode inserted in the corresponding grid hole (C). The artefact generated by the electrode is clearly visible on the image, and it shows that the trajectory is adequate to target the LC.