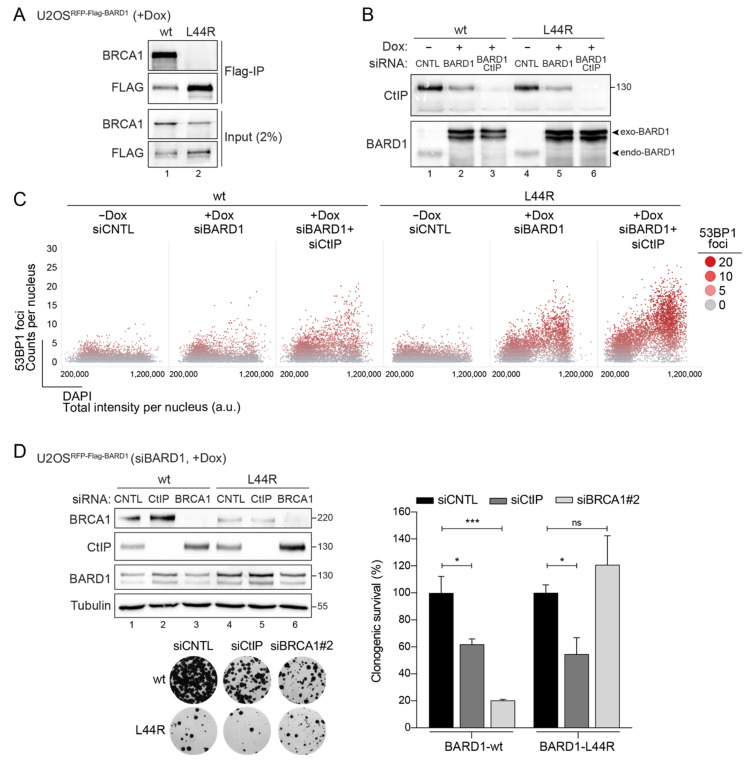
Figure 4.
Synthetic lethality between CtIP and BARD1 occurs independently of the BARD1-BRCA1 interaction. (A) Whole-cell extracts from U2OS Flp-In T-REx cells stably expressing Dox-inducible RFP-FLAG BARD1 wt and L44R variant were subjected to FLAG-immunoprecipitation and subsequently to western-blot with the indicated antibodies. (B) Same cells as in (A) were transfected with siBARD1 in combination with either siCNTL or siCtIP for 48 h were subjected to immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. (C) Same cells as in (B) were fixed and stained for DNA content (DAPI) and 53BP1. The formation of 53BP1 foci was assessed in a cell cycle-dependent manner by high-content quantitative image-based cytometry (QIBC). Scatter plots depict the cell cycle distribution of 53BP1 foci per nucleus. Each dot represents a single cell. (D) U2OS Flp-In T-REx cells stably expressing Dox-inducible RFP-FLAG-BARD1 wt and L44R variant were transfected with siBARD1 in combination with either siCNTL, siCtIP or siBRCA1. At 6 h post-transfection cells were treated with Dox (1 μg/mL). A total of 24 h later, cells were plated at low dilutions (500 and 1000 cells) into 6-well plates and grown for 14 days. Left panel, Protein levels were verified by immunoblotting of the whole-cell lysates. In addition, representative images of survival assay are depicted (1000 cells dilution). Right panel, Bar graph illustrates survival by calculating the colony intensity relative to siCNTL-transfected cells. Data, mean ± s.e.m. (n = 4). Statistical significance was calculated with unpaired t-test. * p value ≤ 0.05, *** p value ≤ 0.001, ns p value > 0.05.