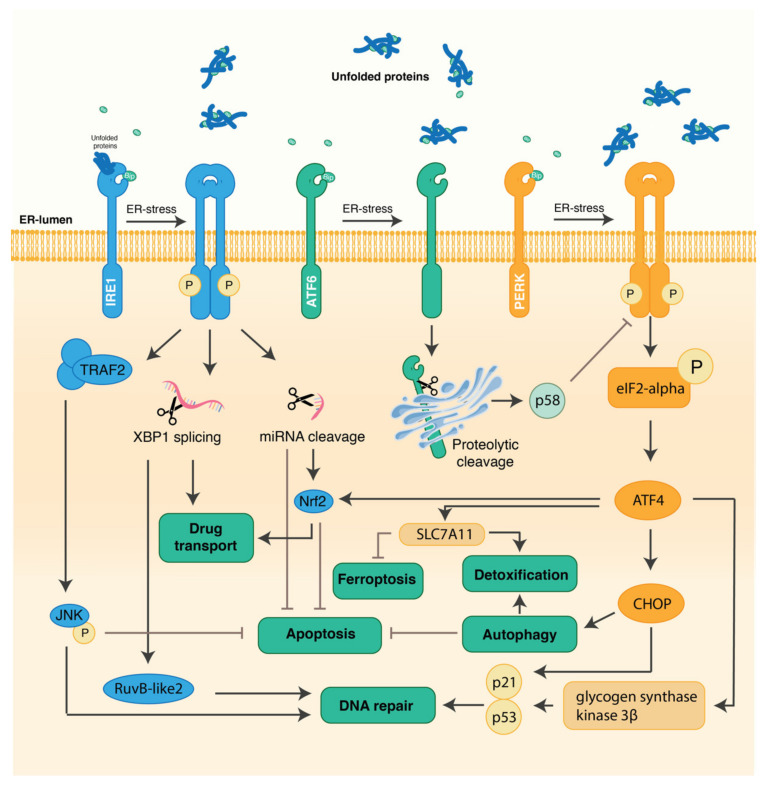
Figure 2.
The accumulation of unfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum lumen induces ER stress, leading to the dissociation of BiP from IRE1α, ATF6, and PERK. This activates the three pathways, resulting in the unfolded protein response, which in turns stimulates many underlying pathways and mechanisms that contribute to increased chemotherapeutic resistance in HCC. IRE1α mainly leads to DNA repair and inhibition of apoptosis trough the activation of the TRAF2/JNK pathway, but also the alteration of drug transport through XBP1 splicing and Nrf2 activation. ATF6 on its turn activates p58 via proteolytic cleavage. Finally, PERK is mainly responsible for the mechanisms activating autophagy through the eif2-alpha/ATF4/CHOP axis and DNA repair (eif2-alpha/ATF4 pathway). It also inhibits ferroptosis via the eif2-alpha/ATF4 pathway.