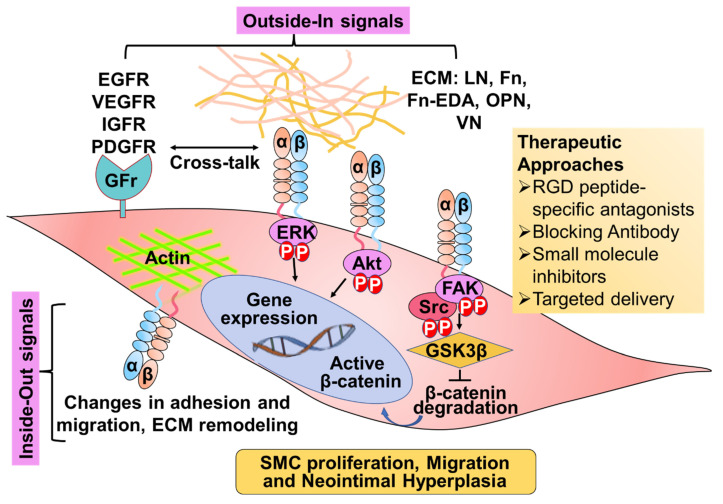
Figure 1.
Schematic showing the signal transduction pathways regulated by integrins in smooth muscle cells (SMC). Depending on the type of integrin and its expression on SMCs, they can trigger signals promoting synthetic or paradoxically a contractile SMC phenotype. Many of the reported SMC-specific integrins promote synthetic SMC phenotype. For example, integrin binding to extracellular matrix (ECM) or activation of growth factor receptors (GFr) facilitates downstream signaling events via FAK-Src, Akt, or ERK pathway, resulting in SMC proliferation and migration and neointimal migration hyperplasia. Abbreviations: ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase; ECM: extracellular matrix; EDA: extra domain A; FAK: focal adhesion kinase, Fn: Fibronectin; IGFR: insulin-like growth factor receptor; LN: Laminin; OPN: Osteopontin; PDGFR: platelet-derived growth factor receptor; VEGFR: vascular endothelial growth factor receptor; VN: Vitronectin.