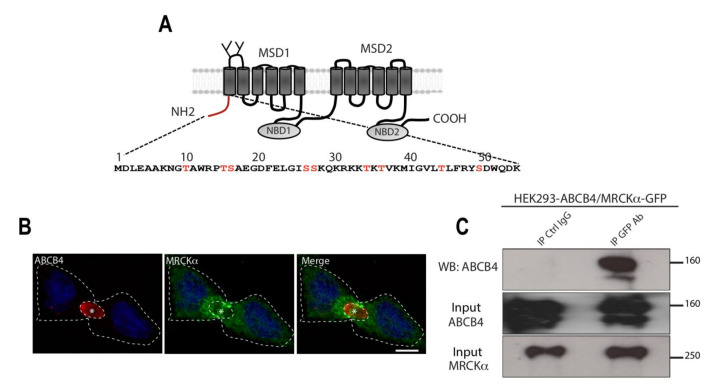
Figure 1.
Colocalization and coimmunoprecipitation of ABCB4 with the serine/threonine kinase MRCKα. (A) Schematic representation of ABCB4. ABCB4 is composed of two membrane-spanning domains (MSD1 and MSD2) and two nucleotide-binding domains (NBD1 and NBD2). The two glycosylation sites in the first extracellular loop are indicated. The amino acid sequence of the intracytoplasmic N-terminal domain of human ABCB4 isoform A (NP_000434.1) is shown. The serine and threonine residues present in the N-terminal domain of ABCB4 and are indicated in red. (B) HepG2 cells transiently expressing ABCB4 were grown on coverslips, fixed, permeabilized, and stained with anti-ABCB4 antibody followed by anti-MRCKα antibody, and then incubated with Alexa-Fluor-594- and 488-conjugated secondary antibodies and visualized by confocal microscopy. Nuclei were stained with DRAQ 5 (Blue). Asterisks indicate bile canaliculi. Bars: 10 mm. (C) HEK-293 cells were co-transfected with plasmids expressing ABCB4 and GFP-tagged MRCKα, and cell lysates were incubated with anti-GFP antibody or mouse immunoglobulin G (IgG) covalently linked to agarose beads. The immunoprecipitated complex was immunoblotted with anti-ABCB4. The presence of MRCKα and ABCB4 in the cell lysate (Input) was detected by immunoblot with anti-MRCKα and anti-ABCB4 antibodies. Presented data were cropped from the full immunoblots shown in Supplementary Figure S1.