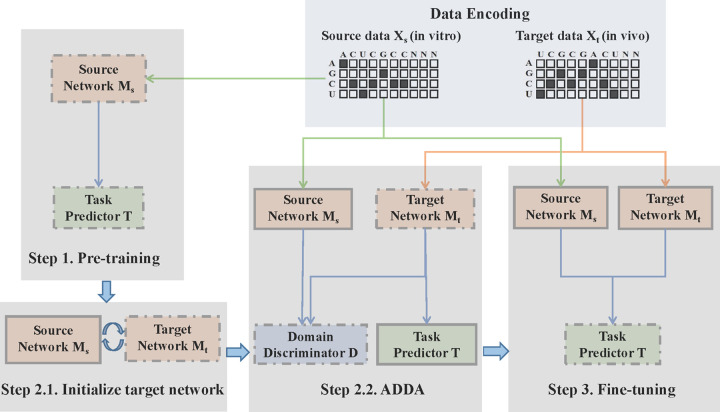
Fig 1. Flowchart of the RBP-ADDA method.
During Data Encoding, each sequence in the sample (in vitro and in vivo) is represented as a concatenation of a one-hot encoding vector representing the nucleotides. Step 1. Pre-training. We use in vitro data to pre-train a source network and task predictor. Step 2.1. Initialize the target network. Target network is initialized by sharing the same parameters and architecture with source network. Step 2.2. ADDA. We apply adversarial learning to train the target network on in vivo data and train the domain discriminator. Step 3. Fine-tuning. We use both the source and target network to fine-tune the task predictor. Solid lines indicate steps in which the network parameters are fixed.