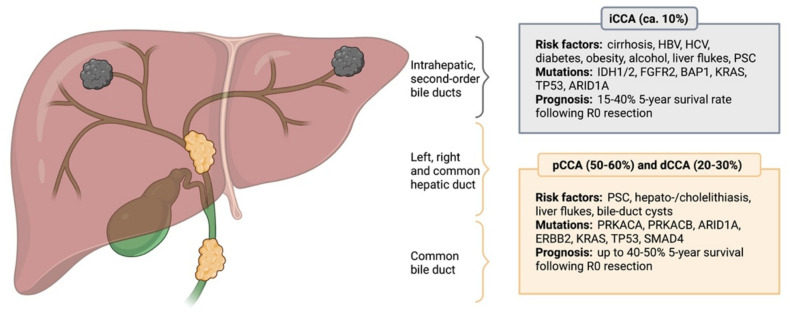
Figure 1.
Anatomical classification of cholangiocarcinoma. CCA is anatomically divided into intrahepatic (iCCA), perihillar (pCCA) and distal (dCCA) cholangiocarcinoma, with pCCA and dCCA being summarized as extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (eCCA). Different CCA subtypes possess distinct molecular aberrations and differ in terms of their etiology, while certain risk factors and genetic mutations are not subtype-specific. The most common risk factors and prevailing genetic alterations are presented. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; PSC: Primary sclerosing cholangitis; IDH1/2: Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1/2; FGFR2: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2; BAP1: BRCA1 associated protein 1; KRAS: Kirsten rat sarcoma virus; TP53: Tumor suppressor protein 53; ARID1A: AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 1A; PRKACA: Protein kinase cAMP-activated catalytic subunit alpha; PRKACB: Protein kinase cAMP-activated catalytic subunit beta; ERBB2: Erb-B2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2; SMAD4: Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4.