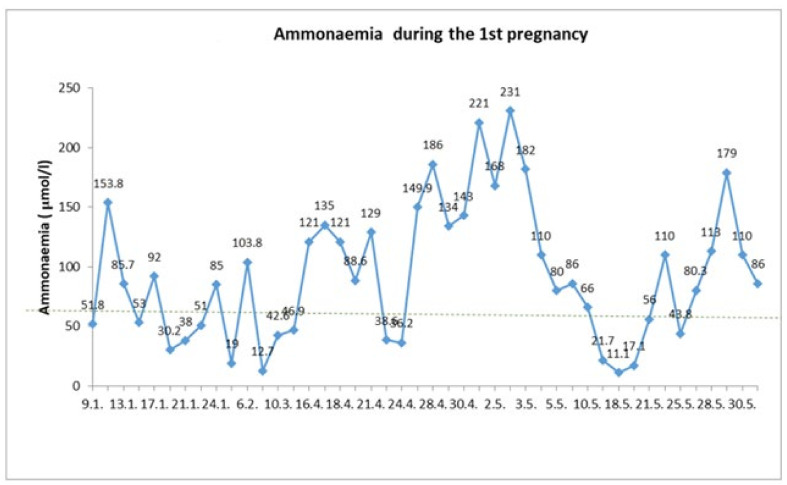
Figure 1.
The course of ammonemia during the first pregnancy. The patient was hospitalized in multiple specialized clinical settings from 16 April until 1 June 2015. Despite the high-energy intake managed by the administration of 20 and 40% glucose infusions and intravenous arginine and sodium-benzoate, the effort to reduce ammonia levels to the normal values (below 60 μmol/L) did not succeed for an extended time. Signs of impaired consciousness on May 2nd and an ammonia level rise to 231 μmol/L resulted in the reinitiation of sodium-phenylbutyrate treatment, which had a transient positive effect on the plasma ammonia level. Despite an unchanged treatment, on May 29th, the ammonia level rose to 179 μmol/L again and the patient reported transient weak fetal movements. Initiation of corticosteroid fetal lung maturation was indicated and on 1 June delivery by C-section was performed due to the potential risk for the mother and her fetus.