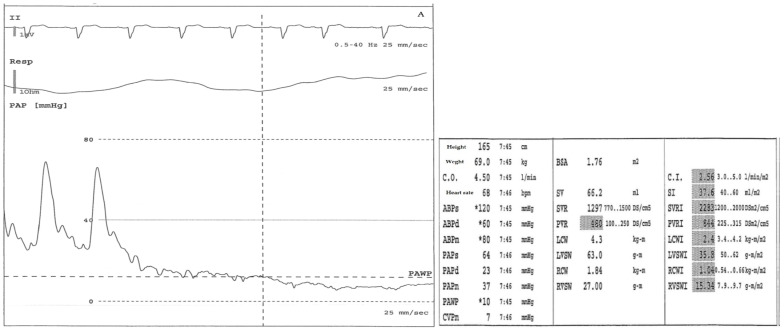
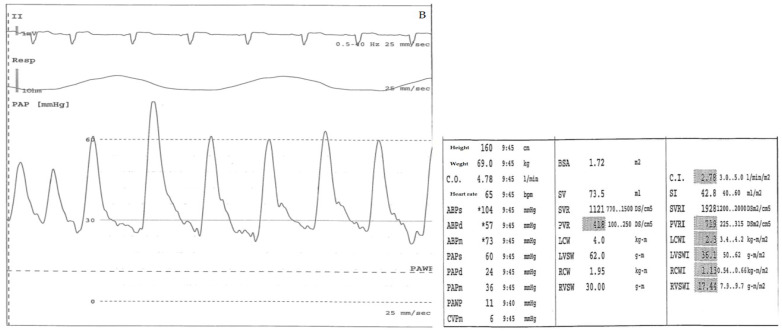
Figure 2.
(A) Right cardiac catheterization in a CTEPH patient, not a candidate for surgical treatment due to the involvement of the distal pulmonary arteries (technically inaccessible), before treatment (as reported in the table at right PVR 480 dynes/s/cm (-5)), * software evaluation. From below: pulmonary arterial pressure, respiratory, and ECG waveforms during arterial catheterization. The first part of the pressure trace reflects the pressure in a pulmonary artery (large swings, dicrotic notch). Then, the balloon is inflated, and the tip of the Swan Ganz catheter floats until it wedges in a small artery (small swings synchronous with respiratory rate). This provides a pulmonary arterial wedge pressure (PAWP), i.e., an indirect measure of the pressure in the left ventricle. (B) Right cardiac catheterization in the same patient after three months of treatment with riociguat as per data sheet (as reported in the table at right PVR 418 dynes/s/cm (-5)).