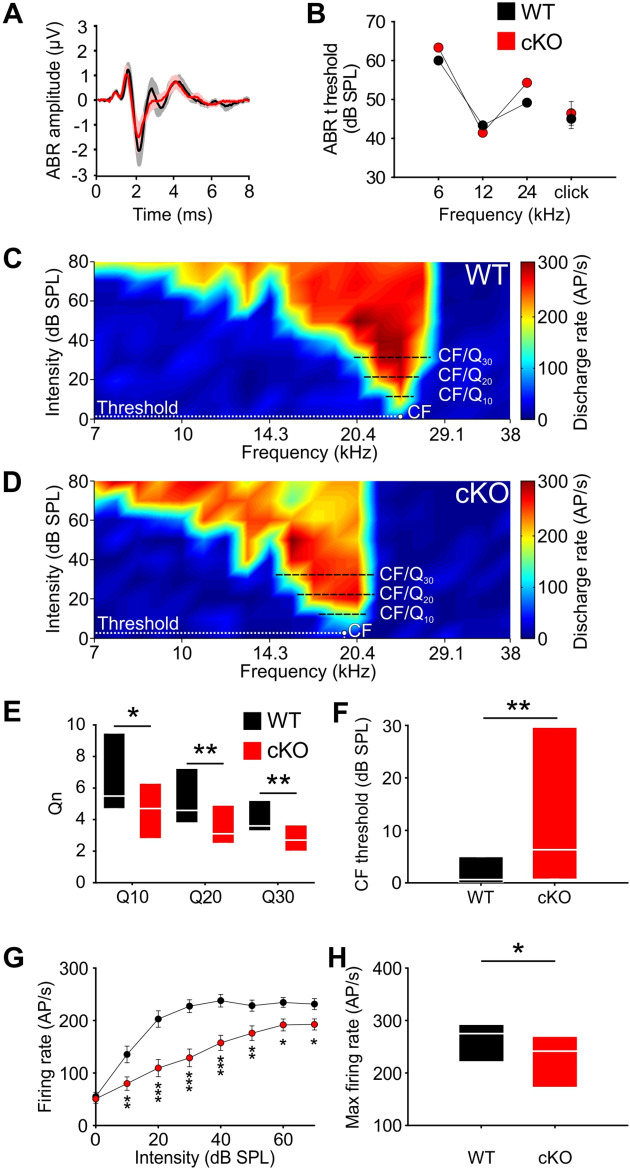
Figure 4. Wildtype and cKO mice show similar auditory brainstem response (ABR) thresholds, but differences in frequency selectivity, response threshold, and maximal firing rate in neurons of the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body (MNTB).
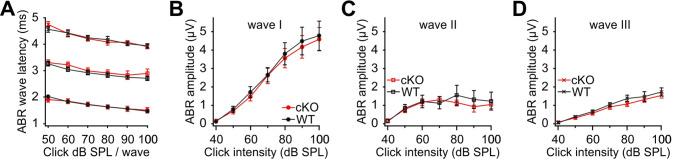
(A) Grand averages of ABR waveforms to 80 dB click stimulation recorded from cKO (red) and wildtype (black) at P13–14. (B) ABR thresholds in response to 6, 12, or 24 kHz tone bursts and click stimuli did not differ between wildtype (n = 7) and cKO (n = 6) at P13–14. For values, see Supplementary file 1b. (C, D) Representative frequency response areas of MNTB neurons (P14) recorded juxtacellularly in a wildtype mouse (C) (characteristic frequencies [CF]: 24 kHz, threshold 0.1 dB SPL, Q10/20/30 = 6.4/4.3/4.2), and in a cKO littermate (D) (CF: 18.4 kHz, threshold = 3 dB SPL, Q10/20/30 = 3.7/3.2/2.8). Note that the response area is broader and that the CF thresholds are increased in cKO. (E) Frequency selectivity of MNTB neurons was reduced in cKO mice as indicated by lower Q-factors (shown are medians and 25%, 75% quartiles [n = 25 WT; n = 32 cKO, P14]; Mann–Whitney rank-sum test: Q10: p=0.03, Q20: p=0.008, Q30: p=0.002). (F) Sound thresholds of individual MNTB neurons are elevated in cKO mice compared to wildtype (p=0.006). (G) Average rate-level functions at CF show decreased action potential firing in cKO at SPLs above 10 dB (two-way ANOVA: effect of strain p<0.001, effect of intensity p<0.001). (H) Maximum firing rates during acoustic stimulation are significantly decreased in cKO mice compared to wildtype littermates (two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test: p=0.015).