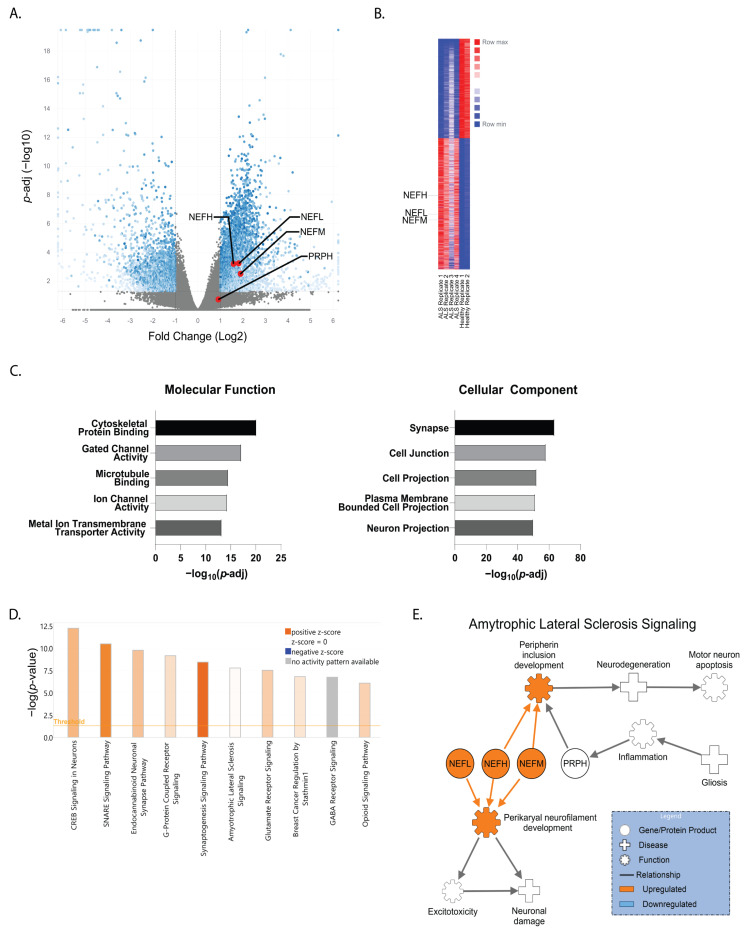
Figure 1.
Comparing neurofilament transcripts and ALS-associated signaling in ALS-discordant twins. (A) Volcano plot and (B) heatmap of differential expression RNA sequencing (DESeq2) comparing the motor neuron transcriptome of an ALS-affected patient (AB) to his non-affected twin (HB). Neurofilament transcripts for neurofilament heavy (NEFH), neurofilament medium (NEFM), and neurofilament light (NEFL) are denoted with red dots and labeled [p-adj < 0.0501 FC ≥ ±1]. For comparison, peripherin (PRPH) was unchanged between the AB and HB. (C) Gene ontology identified the top five molecular functions and cellular components altered in AB motor neurons compared to HB motor neurons [p-adj < 0.0501 FC ≥ ±1]. (D) Ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA) highlighting the ten most affected canonical pathways and (E) the role of altered neurofilament gene transcripts in ALS signaling [p < 0.01; FC > ± 1.35].