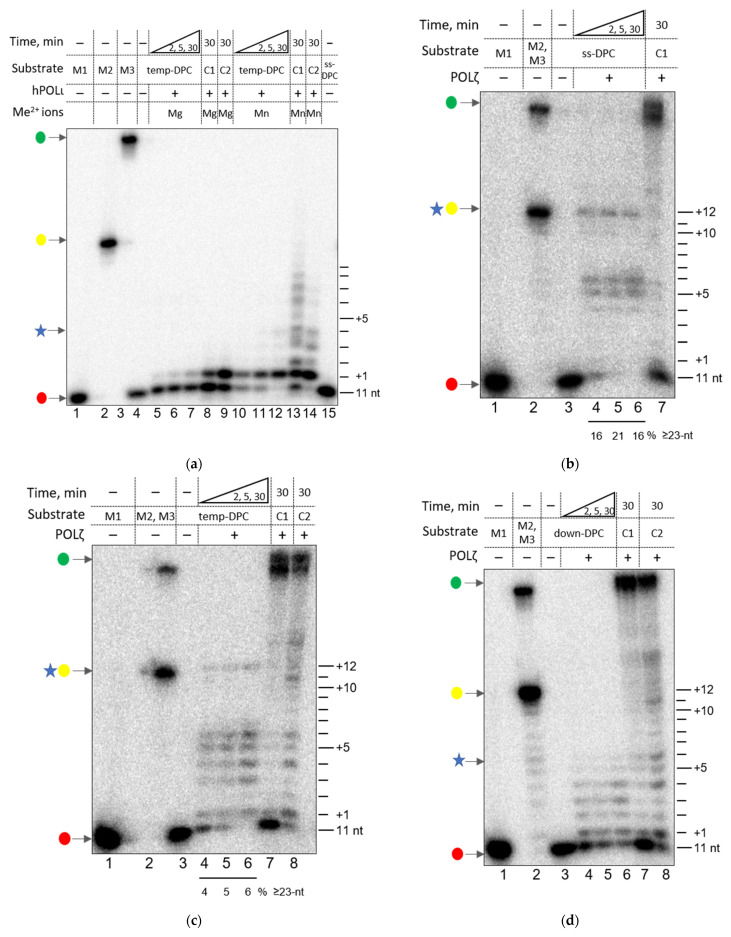
Figure 2.
Primer elongation by hPOLι (a) and yPOLζ (b–d) encountering a DNA protein cross-link. For yPOLζ, panel (b) shows the ss-DPC substrate, panel (c) shows the temp-DPC substrate, and panel (d) shows the down-DPC substrate. The red dots mark the primers, the yellow dots correspond to the synthesis until the cross-link site, and the green dots indicate the full-sized products. The star shows the maximal primer extension on each DPC-containing substrate by each DNA polymerase. Panel (a): lanes 1–3, size markers 11 nt (M1), 23 nt (M2), and 40 nt long (M3); lanes 4 and 15, temp-DPC (lane 4) or ss-DPC substrate (lane 15), no DNA polymerase; lanes 5–7: primer extension for 2, 5, and 30 min, respectively, with Mg2+; lanes 10–12, same with Mn2+; lanes 8–9, primer extension (30 min) on the undamaged primer–template (C1, lane 8) or primer–displaced strand–template substrate (C2, lane 9); lane 13–14, same with Mn2+. Panels (b–d): lanes 1–2, size markers M1, M2 and M3; lane 3, ss-DPC (b), temp-DPC (c) or down-DPC substrates (d), no DNA polymerase; lanes 4–6: primer extension for 2, 5, and 30 min, respectively; lanes 7–8, primer extension (30 min) on the undamaged primer–template (C1, lane 7) or primer–displaced strand–template substrate (C2, lane 8).