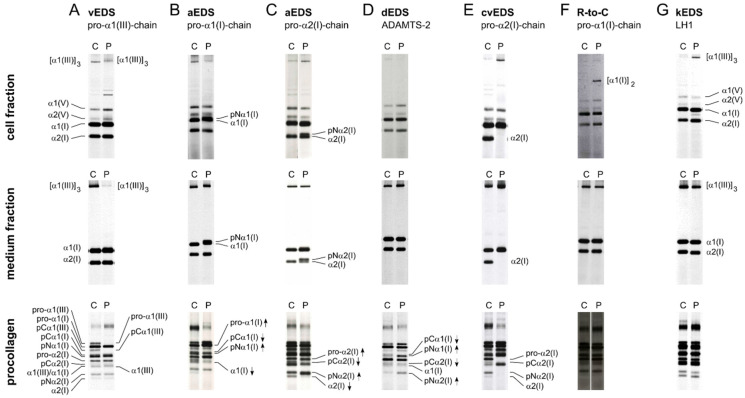
Figure 4.
Illustration of representative (pro)collagen electrophoretic mobility patterns for different EDS types. Metabolically labelled (pro)collagen chains isolated from cells and conditioned medium of dermal fibroblast cultures were either partially digested with pepsin (cell and medium fraction) or left untreated (procollagen) prior to SDS-PAGE. All individual intermediate and mature (pro)collagen chains are indicated on the left side of panel A as a reference. At the right side of the gels, (pro)collagen chains displaying a difference are highlighted. pNα- and pCα-chain denote pro-α-chains that contain only the N- or C-terminal propeptide, respectively. C: control and P: patient. (A) Severely reduced amounts of the type III (pro)collagen homotrimer in the cell and medium fractions in a vascular EDS (vEDS) patient. (B) The presence of additional mutant pNα1(I)-chains, in the cell and medium fractions of patients with arthrochalasia EDS (aEDS) caused by a defect in COL1A1. (C) The presence of additional mutant pNα2(I)-chains, in the cell and medium fractions of patients with arthrochalasia EDS (aEDS) caused by a defect in COL1A2. (D) Accumulation of procollagen chains with a retained N-propeptide (pNα1(I) and pNα2(I)) and nearly complete absence of bands representing the pCα1(I) and pCα2(I) procollagen chains in a patient with dermatosparaxis EDS (dEDS) due to biallelic ADAMTS2 defects. Of note, a normal electrophoretic mobility of the collagen chains is seen in the cell and medium fractions because propeptides are enzymatically removed with pepsin during sample preparation. (E) Complete absence of the α2(I) procollagen chains in cell and medium fractions in a patient with cardiac-valvular EDS (cvEDS). (F) Abnormal disulfide-bonded α1(I) dimers are present in the cell layer but not in the medium fraction of a patient with a pathogenic variant in the COL1A1 gene leading to an arginine-to-cysteine substitution in the α1(I)-chain (c.934C>T, p.(Arg312Cys)). (G) Type I, III and V (pro)collagen chains from a kyphoscoliotic EDS (kEDS) patient with biallelic PLOD1 mutations show a uniformly faster migration in both cell and medium fractions and on procollagen gels, thereby, demonstrating underhydroxylation and underglycosylation of lysyl residues.