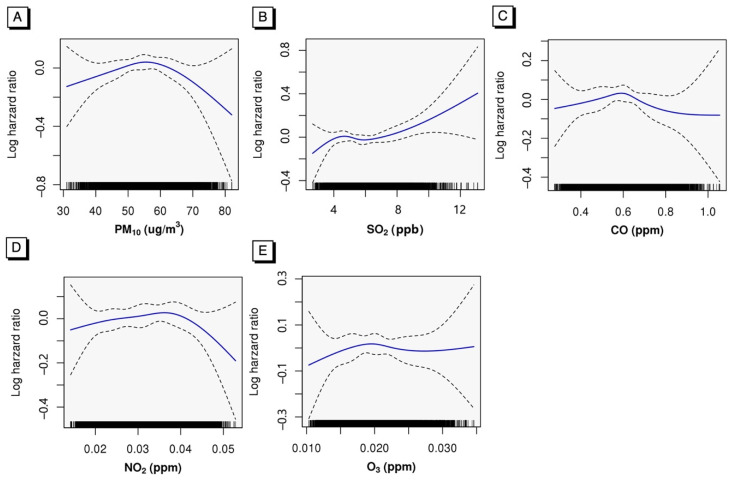
Figure 2.
Log hazard ratio of incidence of osteoporosis-related fracture as a nonlinear curve (solid line) and 95% CIs (dashed lines) of air pollution exposure in the Korean National Health Insurance cohort of adults (age ≥50 y) for (A) PM10, (B) SO2, (C) CO, (D) NO2, and (E) O3. The curves were estimated with Cox proportional hazards models using natural splines with 4 df for PM10, SO2, CO, and NO2, and 3 df for O3. Models adjusted for age, sex, history of rheumatoid arthritis or secondary causes of osteoporosis during the follow-up period, exposure to oral glucocorticoids in the prior year, use of anti-osteoporosis agents, the Charlson Comorbidity Index, household income-based insurance fee, BMI, smoking status, high alcohol intake, and frequency of exercise per week.