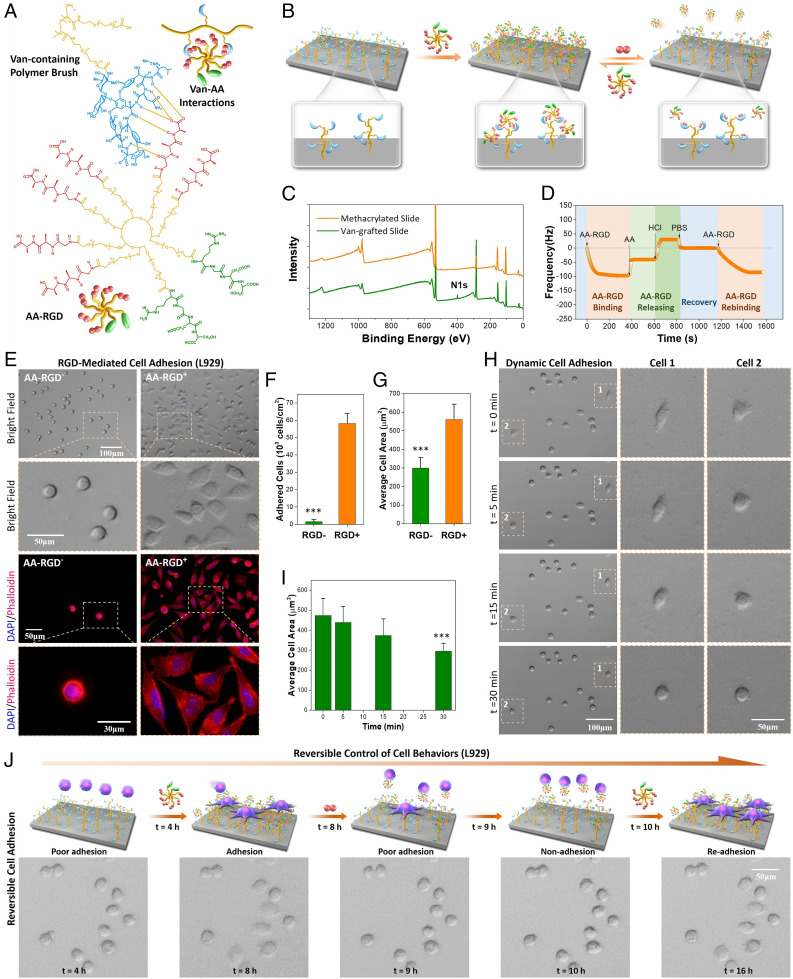
Fig. 2.
Design of dynamic biointerfaces with reversible RGD presentation and dynamic cell adhesion. (A) The multiple Van–AA interactions between the Van-containing polymer brush and cell-adhesive molecule AA–RGD. (B) Reversible presentation of bioactive AA–RGD on the dynamic biointerface. (C) XPS of the quartz slides before and after Van grafting Peak at 400.08 eV indicated the N1 signal. (D) Real-time QCM-D frequency (f) shifts of the Van-containing surface incubated with different solutions. (E) The bright-field and fluorescence images of L929 cells after culture for 4 h on the surfaces without (AA–RGD−) and with AA–RGD (AA–RGD+). (F) Quantitative result of the cell adhesion efficiency. (G) Quantitative result of the average cell-spreading area. (H) Time-dependent L929 cell detachment on the AA–RGD-bound surface after adding 20 mM AA dipeptide. The cell 1 and cell 2 images show a dramatic shrinking in 30 min. (I) The changes of average cell-spreading area during AA-triggered cell detachment. (J) Programmed manipulation of reversible cell adhesion on the dynamic biointerface. ***Statistically significant difference is indicated by P < 0.001 as compared with others.