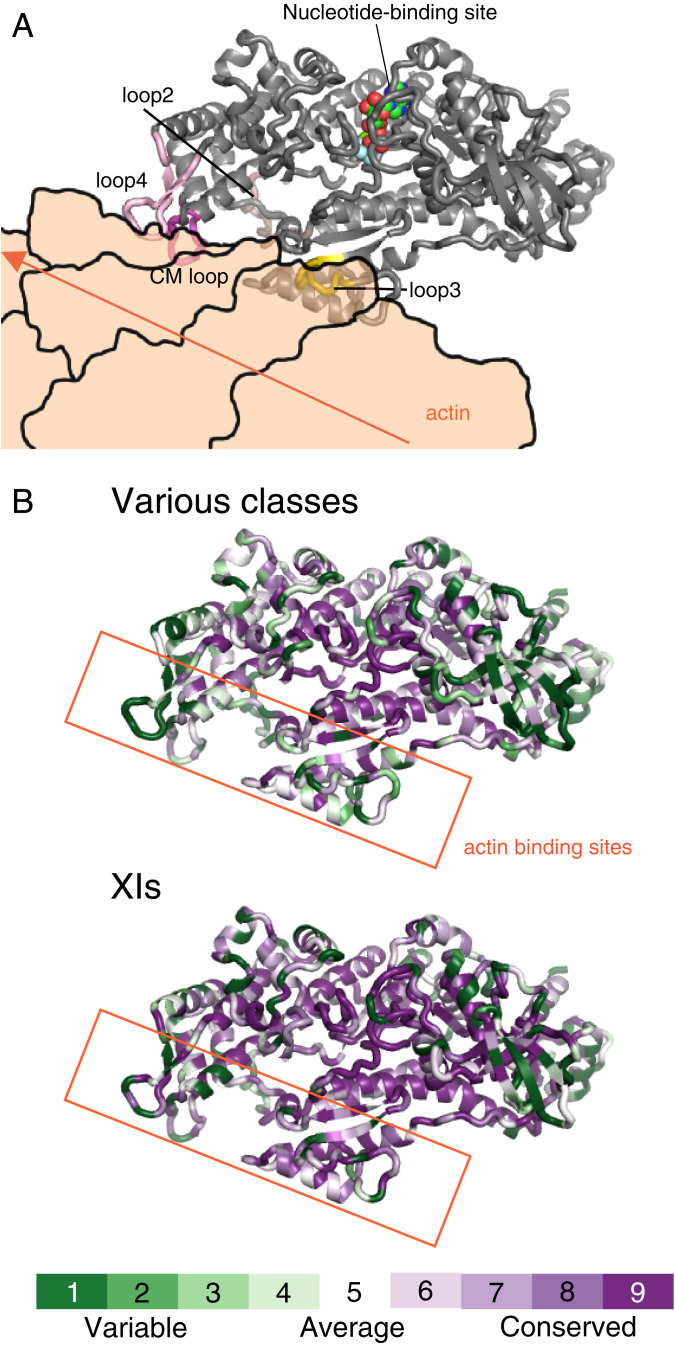
Fig. 5.
Actin-binding region with high amino acid diversity among myosins. (A) Docking model of AtXI-2 MD and actin. This model was created by replacing myosin X in 5KG8 (Rigor myosin X cocomplex with an actin filament) with AtXI-2 MD. The actin in 5KG8 was replaced by 6BNO (structure of bare actin filament). (B) Heat map visualization of AtXI-2 MD showing amino acid conservation and diversity, generated using ConSurf (https://consurf.tau.ac.il/). The conservation score is calculated using the Maximum Likelihood paradigm. The amino acids of myosins are colored by conservation score ranging from green (1, most variable) to purple (9, most conserved residues), as shown in the color legend. The rate was changed to 1 for residues with four or fewer sequence overlaps in the alignment. Various classes showing amino acid comparison of 10 classes of myosins: class I (human Ic and Rat Ib), class II (Dictyostelium II, chicken fast skeletal muscle, chicken smooth muscle, and rabbit skeletal muscle), class V (chicken Va and human Vb), class VI (pig VI), class VII (Drosophila VIIa and mouse VIIb), class VIII (Arabidopsis VIIIa and Arabidopsis VIIIb), class IX (human IXa and human IXb), class X (cow X), class XI (Arabidopsis XI-2, Chara corallina XI, and Chara braunii XI-1), and class XIV (Toxoplasma XIV). XIs showing the amino acid comparison of 18 myosins belonging to class XI: Arabidopsis XI-1, Arabidopsis XI-2, Arabidopsis XI-A, Arabidopsis XI-B, Arabidopsis XI-C, Arabidopsis XI-D, Arabidopsis XI-E, Arabidopsis XI-F, Arabidopsis XI-G, Arabidopsis XI-H, Arabidopsis XI-I, Arabidopsis XI-J, Arabidopsis XI-K, Chara corallina XI, Chara braunii XI-1, Chara braunii XI-2, Chara braunii XI-3, and Chara braunii XI-4.