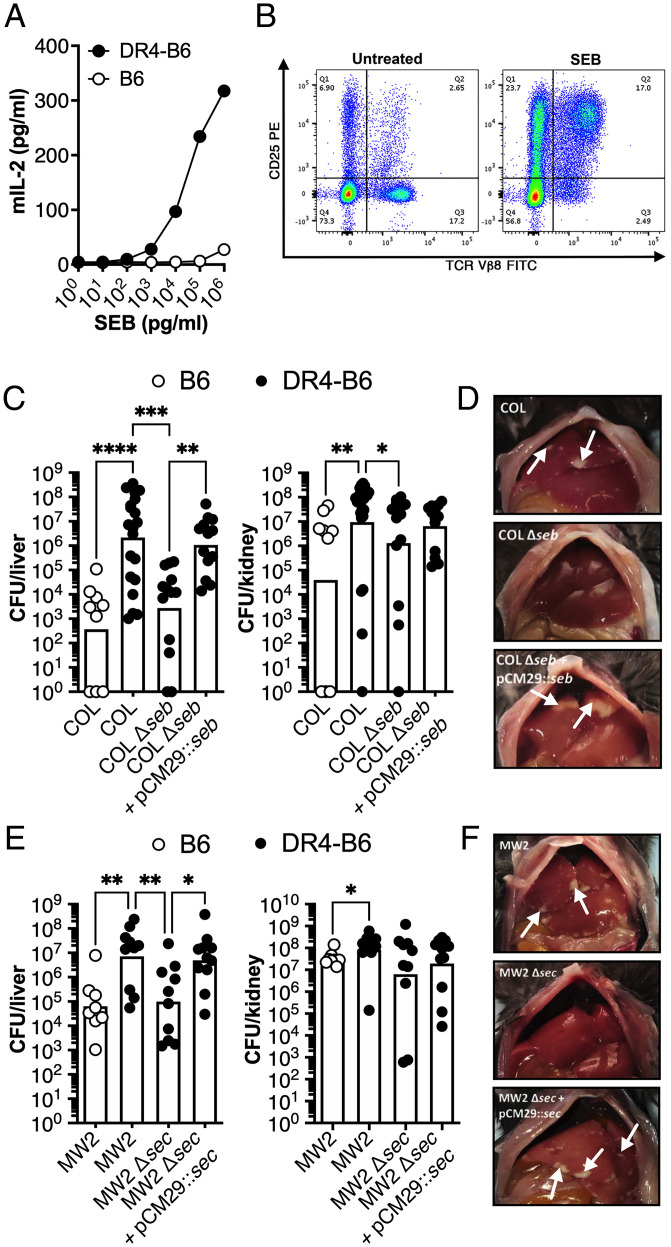
Fig. 1.
SAgs SEB and SEC promote pathogenesis of S. aureus bacteremia in transgenic HLA-DR4 B6 animals. (A) IL-2 production of isolated splenocytes from conventional B6 (open dots) and transgenic DR4-B6 (solid dots) mice following stimulation with a titration of SEB protein. Data shown are from a representative experiment. (B) Activation of Vβ8+ T cells in DR4-B6 mice stimulated by SEB compared to an untreated control as determined by CD25 expression (quarter values represent total cell population). (C–F) B6 and DR4-B6 animals were inoculated i.v. with 5 × 106 CFUs and then killed at 96 hpi for S. aureus COL (C and D) and 72 hpi for S. aureus MW2 (E and F). Liver and kidney bacterial burden (C and E) was assessed in conventional B6 mice (open dots) or in transgenic DR4-B6 mice (solid dots). Each dot represents an individual mouse, and the bar indicates the geometric mean. Significant differences were determined using the Kruskal–Wallis test with the uncorrected Dunn’s test for multiple comparisons (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001). Representative livers from the infected mice from S. aureus COL and mutants (D) and S. aureus MW2 and mutants (F) with white arrows indicate the presence of liver lesions.