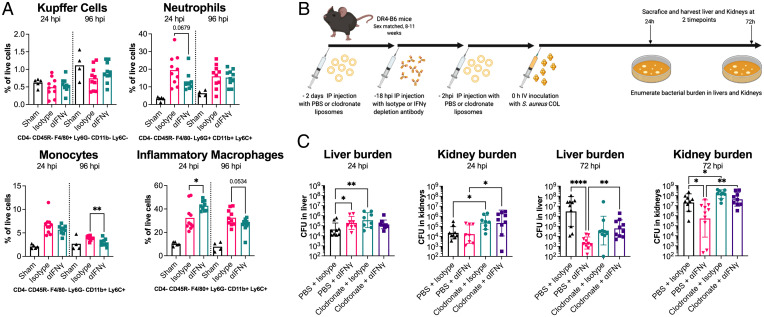
Fig. 6.
Liver macrophages are the target of pathogenic IFN-γ production. (A) Flow cytometry–based phenotyping of immune cells isolated from livers of mice infected with S. aureus strain COL at 24 and 96 hpi. Control animals (sham) were treated with HBSS only. Cells were defined based on the staining profile listed below each graph and normalized to the percentage of live cells. Isotype antibody and αIFN-γ treatments were compared; each dot represents an individual mouse, and the bar indicates the mean. Significant differences were determined using an unpaired Welch’s t test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). (B) Schematic outlining Clodronate liposome-based depletion of macrophages along with IFN-γ depletion used prior to i.v. infection of mice with S. aureus COL. (C) Bacterial burden in liver and kidneys at 24 and 72 hpi is shown. Each dot represents an individual mouse, and the bar represents the geometric mean for CFUs/organ. Significant differences were determined using the Kruskal–Wallis test with the uncorrected Dunn’s test for multiple comparisons (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001).