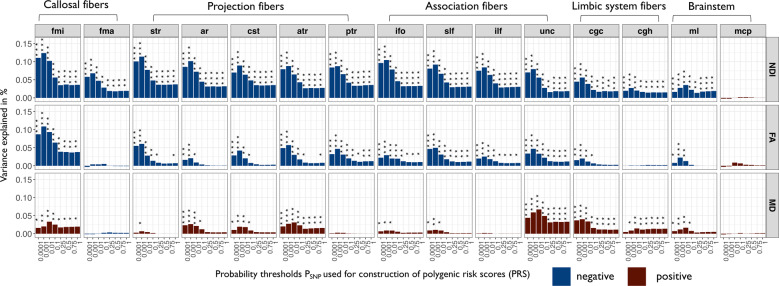
Fig. 5. Associations between polygenic risk scores for schizophrenia and white matter tracts.
Barcharts of variance explained by schizophrenia PRS (R2, y-axis) constructed at each of eight probability thresholds (0.0001 ≥ PSNP ≤ 1, x-axis) for each of three white matter metrics (NDI neurite density index, FA fractional anisotropy, MD mean diffusivity) measured at 15 major white matter tracts: mcp middle cerebellar peduncle, ml medial lemniscus, cst corticospinal tract, ar acoustic radiation, atr anterior thalamic radiation, str superior thalamic radiation, pts posterior thalamic radiation, slf superior longitudinal fasciculus, ilf inferior longitudinal fasciculus, ifo inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus, unc uncinate fasciculus, cgc cingulate gyrus part of cingulum, cgh parahippocampal part of cingulum, fmi forceps minor, and fma forceps major. Blue bars indicate negative associations and red bars positive associations; asterisks indicate P values for association after FDR correction: *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001. Polygenic risk scores for schizophrenia were significantly associated with NDI, FA, and MD of multiple white matter tracts.