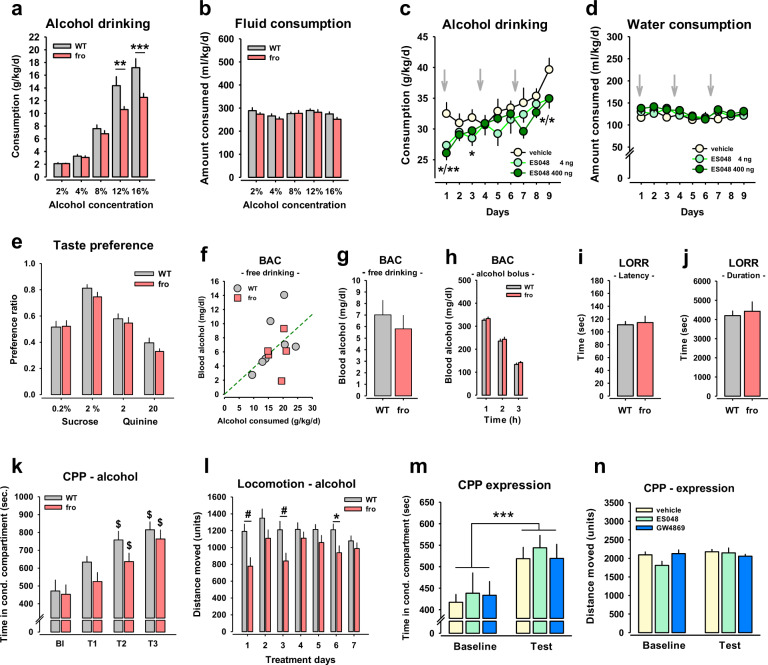
Fig. 2. Neutral sphingomyelinase-2 (NSM) controls alcohol consumption, but not sedating and conditioned reinforcing effects in mice.
a Mice with a heterozygous NSM knock out (fro) show reduced alcohol consumption in a two-bottle free-choice paradigm compared to wild type (WT) controls. b Lack of NSM function did not affect total fluid consumption in mice. Data are expressed as means ± s.e.m. (n = 8 per group; **P < 0.001; ****P < 0.001 vs. WT). c Alcohol drinking was reduced in C57Bl6J mice in a two-bottle free-choice drinking test by repeated treatment with the NSM inhibitor ES048 (i.p., grey arrows). d No effect of the ES048 treatment was observed on water consumption in these animals. Data are expressed as means ± s.e.m. (n = 10 per group; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 vs. vehicle control). e No role of NSM in taste preference. f, g Free-choice alcohol drinking yielded a proportional blood alcohol concentration (BAC) in heterozygous NSM deficient mice (fro) and wild type (WT) mice at individual level (n = 7 per group). h No difference in BAC after bolus injection of alcohol (3g/kg, i.p) in fro and WT mice (n = 9–10 per group). i, j Lack of NSM function has no effect on the sedating properties in the loss of the rightening reflex (LORR) of a single alcohol injection (3.5 g/kg; i.p.) as shown in latency and duration of sedating effects (n = 9 per group). k NSM has no role in the establishment of the conditioned reinforcing effects of alcohol in mice in a conditioned place preference (CPP) test, but (l) is required for locomotor activating effects of alcohol (2 g/kg, i.p.; Bl baseline, T test trial). Data are expressed as means ± s.e.m. (n = 11–15 per group; $P < 0.05, vs. BL). m NSM is not involved in the expression of the conditioned reinforcing and conditioned locomotor effects of alcohol in mice as the two NSM inhibitors GW4869 and ES048 applied before CPP retrieval, did not affect CPP expression or (n) conditioned locomotor effects. Data are expressed as means ± s.e.m. (n = 9–10 per group; ***P < 0.01, ANOVA, effect of test trial).