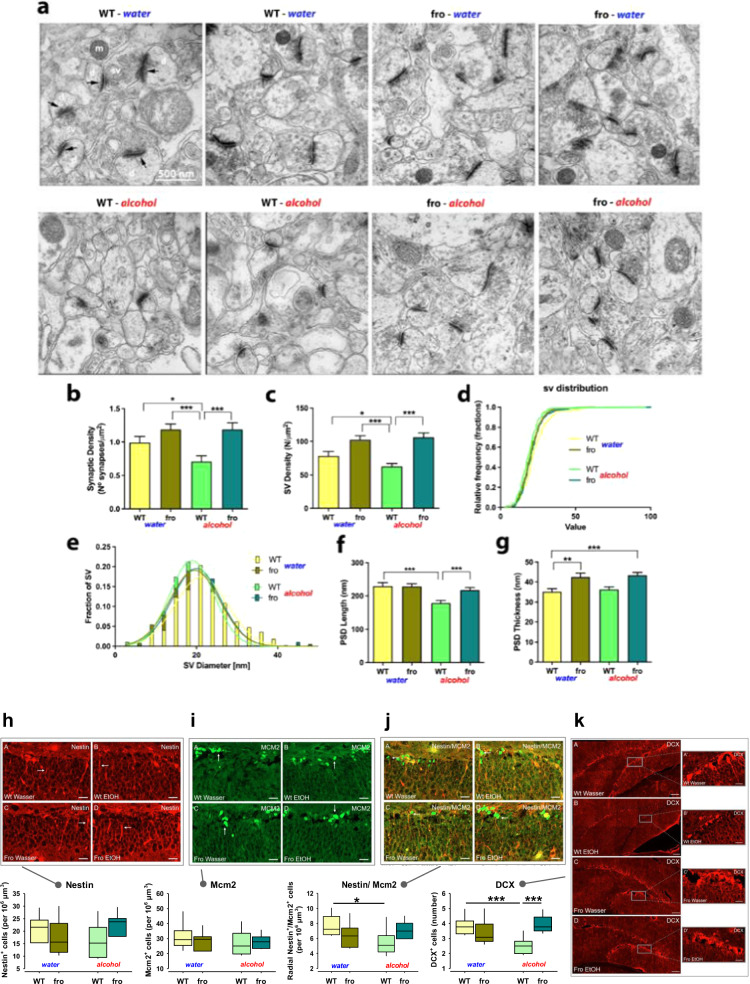
Fig. 6. Neutral sphingomyelinase-2 (NSM) controls synaptic structure of mice and changes after alcohol (EtOH) consumption.
a Representative electron micrographs of synapses in the dorsal hippocampus (DH) CA1 region in fro and wild type (WT) mice (black arrows indicate post-synaptic densities; d dendrite, sv synaptic vesicles, m mitochondria). b Synaptic density. c Synaptic vesicle density (n = 53 synapses). d, e Synaptic vesicle diameter (363 WT, 274 WT + EtOH, 589 fro and 654 fro + EtOH) vesicles. f Post-synaptic density length (46 WT, 58 WT + EtOH, 72 fro and 72 fro + EtOH post-synaptic densities). g Post-synaptic density thickness. Data are expressed as means + s.e.m. (n = 3 per group; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001). h–k Female fro mice do not show altered neurogenesis in the DH, but reduced susceptibility to the suppressive effects of alcohol (n = 4 per group; DCX-doublecortin). Data are expressed as means + s.e.m. (*P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001).