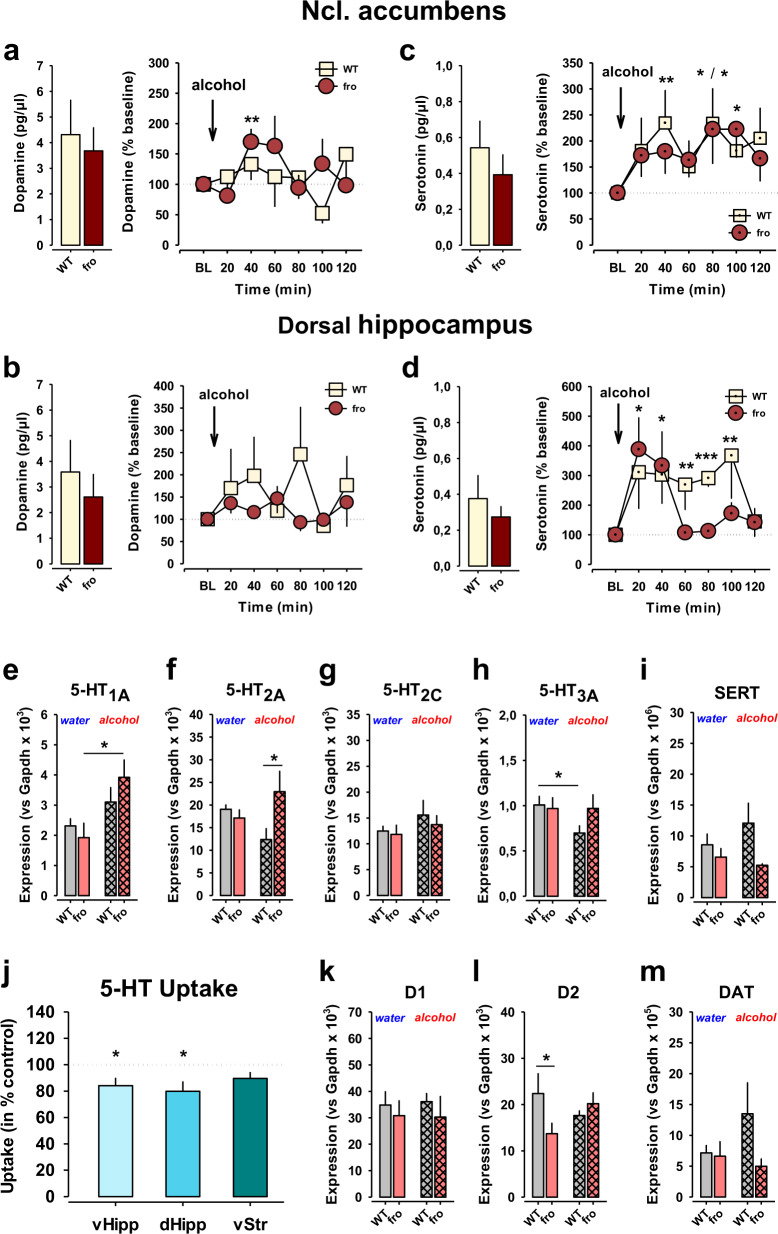
Fig. 7. Neutral sphingomyelinase-2 (NSM) controls monoaminergic signalling in the brain.
a–d Reduced NSM activity in mice (fro) has no effect on basal extracellular levels of dopamine (DA) and serotonin (5-HT) in the nucleus accumbens (Nac) and dorsal hippocampus (DH), but enhances DA response to alcohol (2 g/kg, i.p.) in the Nac (n = 16–27 per group). Data are expressed as means + s.e.m. of percent baseline (BL) (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 vs. BL). e–i Effects of reduced NSM function and alcohol drinking on regulation of 5-HT receptor and transporter (SERT) mRNA expression in the ventral striatum (vStr) of mice. j Sphingomyelinase treatment inhibits 5-HT uptake in synaptosomes from ventral hippocampus (vHipp), dorsal hippocampus (dHipp), but less so in the vStr of mice. Values are expressed as percent of control ± s.e.m. (n = 5–9 per group). Data are expressed as means + s.e.m. of control levels taken as 100% (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 vs. control). k–m Effects of reduced NSM function and alcohol drinking on regulation of dopamine D1 and D2 receptor and transporter (DAT) mRNA expression in the vStr of mice (n = 3–6 per group). Data are expressed as means + s.e.m. (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01).