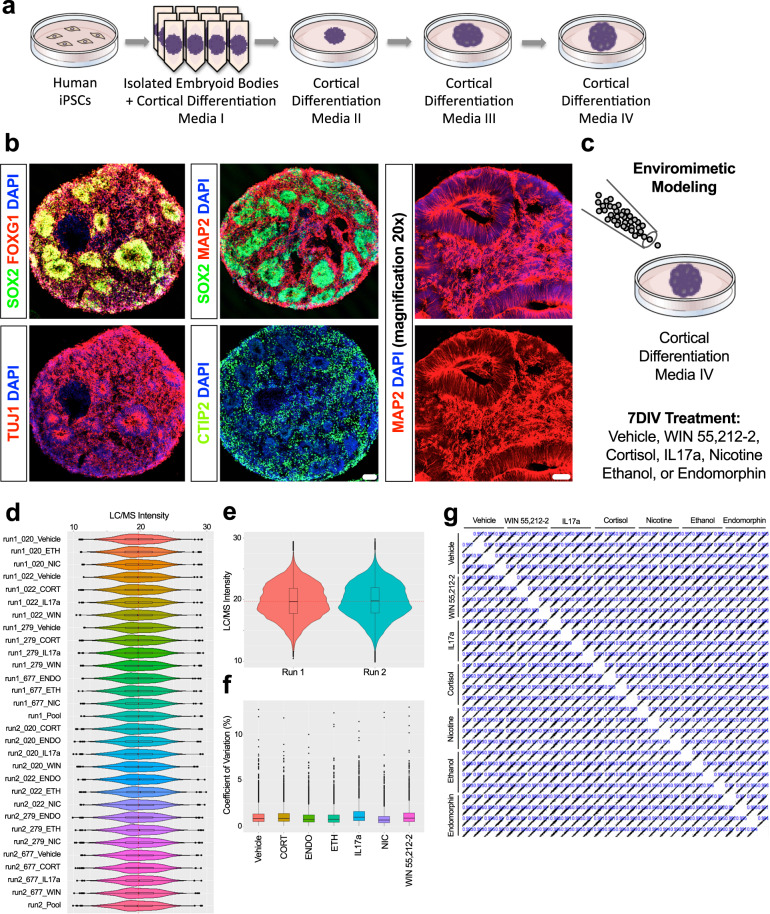
Fig. 1. Enviromimetic forebrain organoids exhibit robust reproducibility.
a Schematic of Human-Derived Dorsal Forebrain Organoid Culturing Pipeline. To generate dorsal forebrain organoids, iPSCs from healthy adult donors were expanded, dissociated into a single-cell suspension, and transferred to ultra-low adherence V-bottom plates. This allowed dissociated iPSCs to proliferate in-suspension to yield highly uniformed (i.e., size constricted) embryoid bodies that were morphologically consistent across wells, plates, and biological donors. In subsequent culturing stages, embryoid bodies were transferred to ultra-low adhesion 6 cm dishes and sequentially transferred through a series of cortical differentiation media (CDM2–4). b Human-Derived Organoids Exhibit Robust Neural Induction and Prototypical Forebrain Developmental Markers Consistent with Early Corticogenesis. As a quality control checkpoint, a pseudorandom assortment of human-derived dorsal forebrain organoids were sampled, drop-fixed, cryosectioned, and immunostained for prototypical forebrain developmental markers. Given the pre-established construct validity of this model, we focused our quality control assessments on the expression of neural stem cells (SOX2 + ; green), forebrain-specific progenitors (FOXG1 + ; red), pan-neuronal markers (TUJ1 + and MAP2 + ; both red in relevant panels), and forebrain-specific early-born neurons (CTIP2 + ; green). This evaluation revealed the expected morphologies of forebrain-specific organoids (e.g., the presence of ventricles, ventricular zones, and developing cortical plates). In addition, all neural-related and forebrain-specific antigens were observed in cultures from all biological donors, indicating the successful assumption of a restricted dorsal forebrain fate. c Schematic of Enviromimetic Treatment Regime. To model exposure to our various narcotic and neuropsychiatric-related enviromimetic risk factors, we chronically treated human-derived dorsal forebrain organoids with a variety of widely-utilized compounds used to study the acute and/or developmental effects of drug exposure and/or environmental risk factors related with mental illnesses. More specifically, this comprised a 7DIV exposure to the cannabinoid receptor agonist WIN 55,212-2, the maternal risk factor IL17a, the human stress hormone cortisol, nicotine, ethanol, and the μ-opioid agonist endomorphin. To ensure consistency across conditions and biological donors, treatments were simultaneously administered to parallel batches of organoids that had been generated from the same originating pool of iPSCs for each human donor. Likewise, all human donor samples were cultured simultaneously and maintained in parallel. d Box plots of Raw TMT-LC/MS Intensities Indicates Robust Reproducibility of 3D Organoid Cultures Across Biological Donors and Replicates. To unbiasedly establish the reproducibility of our culturing pipeline, we adapted cutting-edge Tandem Mass Tag (TMT) chemistry and high-performance liquid-chromatography/mass-spectrometry (LC/MS) to computationally map the molecular composition of human-derived 3D dorsal forebrain organoids from an isobarically-barcoded condensed pool. This real-time detection strategy thus reduces technical noise and variation, and enables rapid high-content sampling of our various treatment conditions. Our TMT-LC/MS dataset identified 40,452 peptides that could be mapped to 5,120 proteins. Based on statistical thresholds and expression levels, 4857 of these proteins could be quantified. Here we present raw TMT-LC/MS intensities for all individual human donors including all possible permutations relating to our enviromimetic treatment conditions. As shown, the distribution of TMT-LC/MS intensities was extremely similar across all groups and biological donors, indicating robust reproducibility of our 3D dorsal forebrain organoids across all biologics and conditions. e Violin Plots of Raw TMT-LC/MS Intensities Reveal No Evidence of Batch Variance. Because of the large number of samples studied here (n = 30 samples in total including pools/internal references, comprising n = 28 human samples for analysis), our TMT-LC/MS analysis had to be split into two 16-plex runs. We therefore sought to determine the reproducibility of our raw TMT-LC/MS datasets across distinct batches of organoids, donors, and treatment conditions. Splitting raw TMT-LC/MS intensities as a function of batch revealed that raw TMT-LC/MS intensities exhibited remarkably similar distributions as denoted in violin plots provided in (1e). f Comparable Coefficients of Variation Across Protein Intensities of All Groups. We next sought to compute coefficients of variation for protein intensities to examine the relative variability within and between our various narcotic and neuropsychiatric-related enviromimetic treatment groups. This analysis once more revealed that all groups exhibited similar coefficients of variation in protein expression, further indicating that our 3D dorsal forebrain cultures remained reproducible even after accounting for divergences in treatment allocation. g Correlation Matrix of All Donors and Groups Confirm Sample Reproducibility. Last, generation of a stringent correlation matrix revealed that there was robust correlation within treatment groups (oftentimes, r2 > 0.99) as expected. In sum, this unbiased statistical analysis confirmed that our culturing pipeline yielded reproducible 3D dorsal forebrain tissue across donors, conditions, and independent batches. For all panels, each donor sample was treated with all experimental compounds. This yielded n = 4 iPSC donors x n = 7 treatment groups for a total n of = 28 experimental samples for LC/MS analysis. Scale bar in b = 100 μm for whole organoid images and 60 μm for ×20 magnification of MAP2 immunostaining.