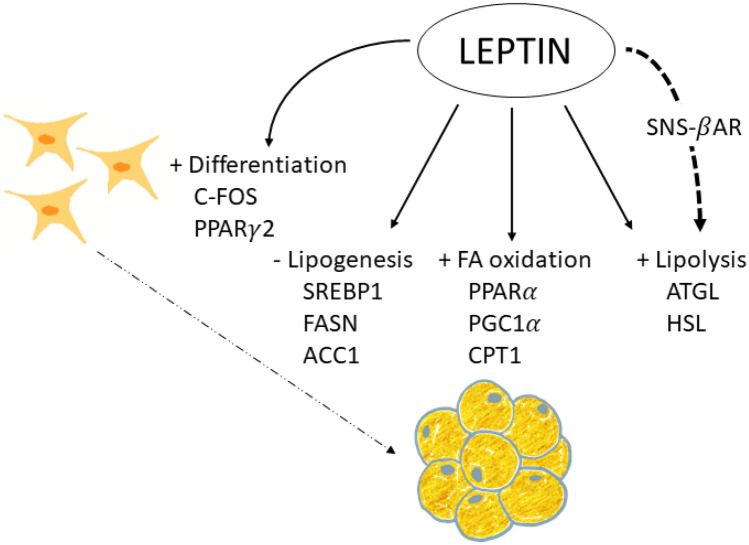
Fig. 1.
Leptin action on lipid metabolism and adipogenesis. Leptin is able to activate lipolysis in white adipose tissue (WAT), by the increase of ATGL (adipose triglyceride lipase) and HSL (hormone sensitive lipase) expression, both acting centrally activating sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and by a direct action on WAT, through β-adrenergic receptors (β-AR). Moreover, leptin directly stimulates fatty acid (FA) oxidation, by the increase of the expression of the genes coding for PPARα (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha), PGC1α (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1alpha) and CPT1 (Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1), among other proteins, and downregulates lipogenesis, decreasing the expression of SREBP1 (sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1), FASN (fatty acid synthase), ACC1 (acetyl-CoA carboxylase), etc., in WAT. In addition, leptin has been shown to exert direct actions stimulating pre-adipocyte differentiation, mainly through the activation of PPARγ2 (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma 2) and C-FOS, into mature adipocytes