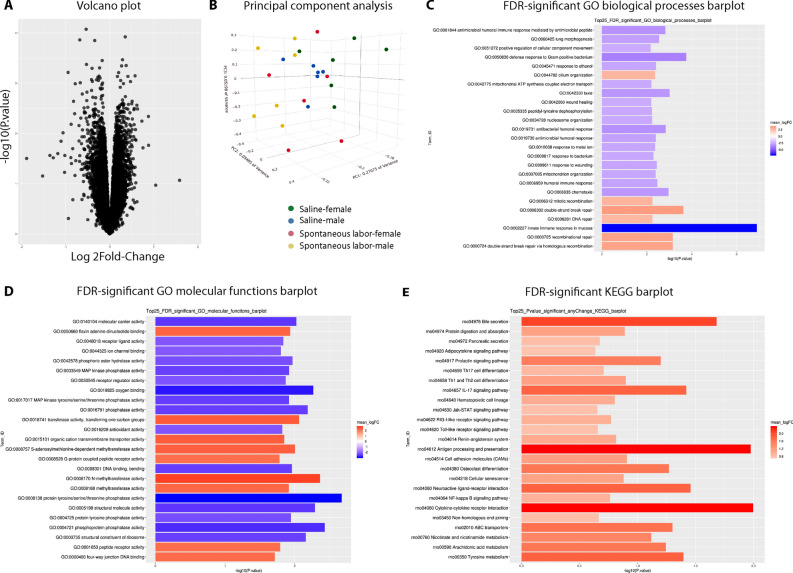
Figure 4.
Impact of anesthesia and surgery on the newborn cortical transcriptome. (A) Volcano plot showing the absence of significantly differentially expressed genes between the spontaneous labor vs. saline pump groups (n = 6/treatment condition from 3 litters each). (B) Principal component analysis (PCA) showing that the major source of variance is not the treatment condition but the sex of the offspring, albeit not significant (green: saline/female, blue: saline/male, red: spontaneous labor/female, yellow: spontaneous labor/male). (C, D) Top 25 false discovery rate-adjusted significantly up- and downregulated genes for Gene Ontology (GO) biological processes (C) and molecular functions (D) after labor induction with Oxt. (E) Significantly upregulated genes with Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis. GO and KEGG analyses revealed a differential impact of anesthesia and surgery on multiple pathways, mostly related to oxygen binding and the immune response, respectively. Therefore, for the rest of our experiments, we used saline pump-implanted dams that eventually labored spontaneously as controls, instead of dams that labored spontaneously without exposure to anesthesia and surgery. The mean log twofold-change in the GO and KEGG barplots are the mean log twofold-change of the genes within the term versus the mean log twofold-changes of the genes in the background using the GAGE method of testing log twofold-changes for perturbations in expression.