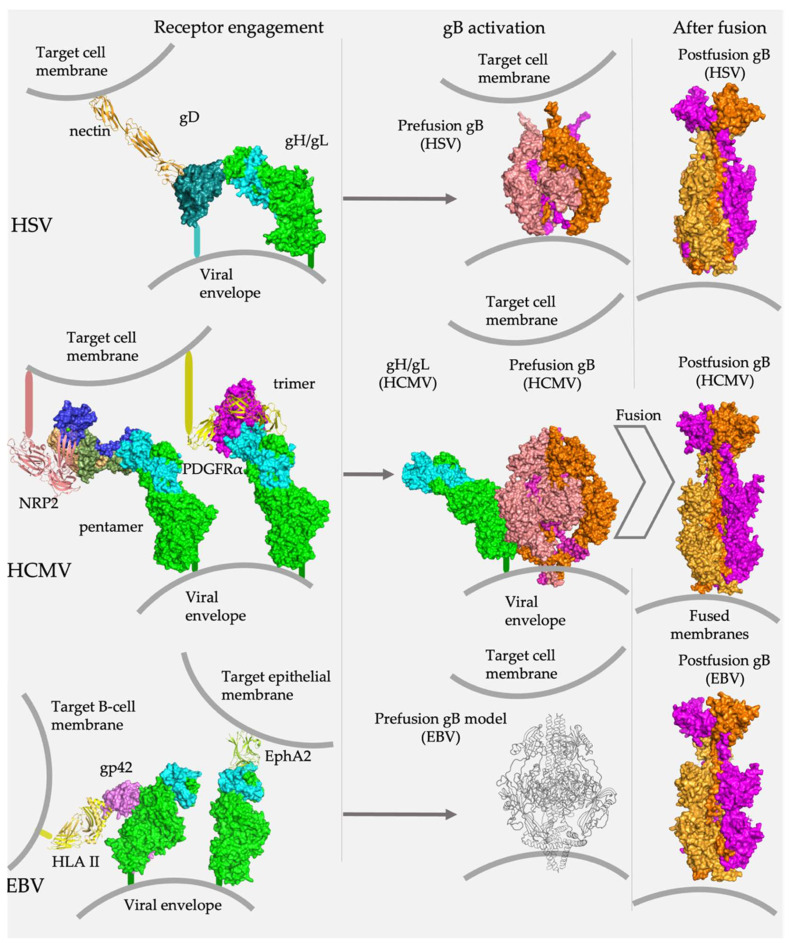
Figure 1.
gH/gL is a central player in herpesvirus entry. Across all subfamilies, gH/gL connects binding of host cell receptors with membrane fusion. In alpha- and betaherpesviruses, gH/gL binds receptor-binding accessory proteins, HSV gD and HCMV gO and UL128/UL130/UL131. In gammaherpesviruses, gH/gL either binds a receptor-binding accessory protein (EBV gp42) or directly engages the host cell receptor (EphA2). In all cases, gH/gL interacts with gB, presumably, relaying the “trigger” signal that leads to the conformational rearrangements that effect membrane fusion. Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics Protein Data Bank Identifiers (RCSB PDB IDs) [27]: gD/nectin (4MYW) [28], HSV-2 gH/gL (3M1C) [29], HCMV gH/gL/gO (7LBE) [30], HCMV gH/gL/UL128/UL130/UL31 (5VOB) [31], EBV gH/gL/EphA2 (7CZE) [32], prefusion HSV gB (6Z9M) [33], postfusion HSV gB (2GUM) [24], prefusion HCMV gB (7KDP) [34], postfusion HCMV gB (5CXF) [35], postfusion EBV gB (3FVC) [36]. The structure of HCMV gH/gL was extracted from the HCMV gH/gL/UL128/130/131 complex (5VOD). The structure of EBV gH/gL/gp42/HLA II was assembled from gH/gL/gp42/E1D1 (5T1D) and gp42/HLA II (1KG0). The schematic of prefusion EBV gB was modeled on the HCMV prefusion gB structure.