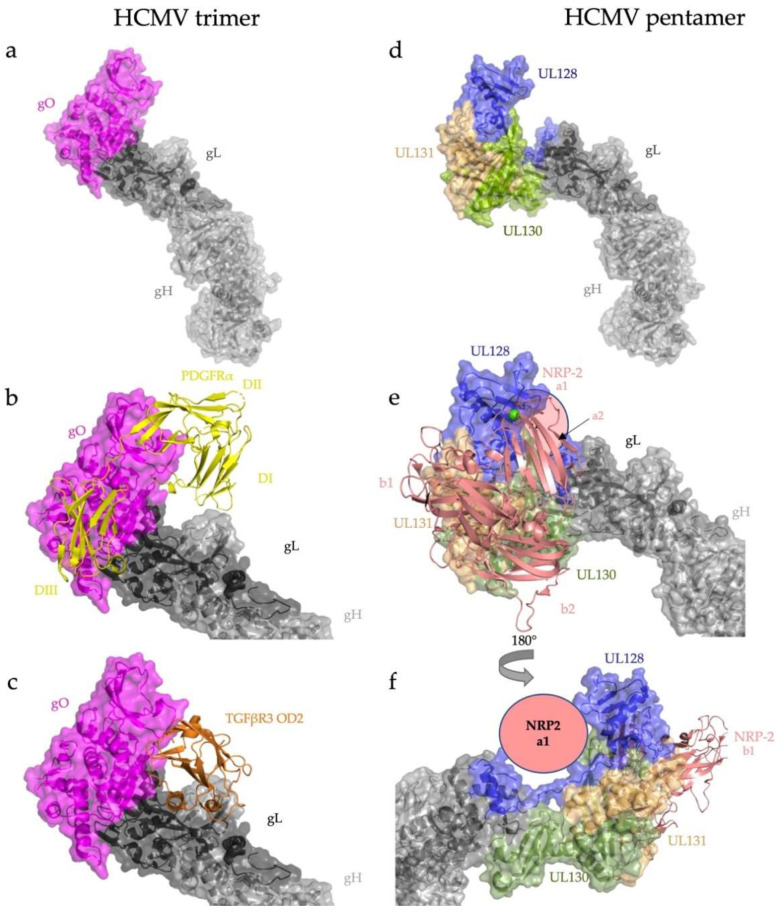
Figure 3.
HCMV engages its host cell receptors almost exclusively through the N-terminal adaptors of the trimer and pentamer. (a) Overall architecture of the HCMV trimer, gH/gL/gO. The adaptor gO attaches covalently to gL. (b) Trimer bound to PDGFRα. PDGFRα domains I-III wrap around gO with minimal contacts with the gH/gL heterodimer itself. (c) Trimer bound to TGFβR3. TGFβR3 domain OD2 binds almost exclusively to gO. (d) Overall architecture of the HCMV pentamer, gH/gL/UL128/UL130/UL31. (e) NRP2 domains a2, b1, and b2 bury a substantial surface across the three components of the pentamer adaptor subcomplex (UL128/130/131), with minimal contact with the gH/gL heterodimer. (f) NRP2 domain a1 contacts the C terminus of gL (shown schematically). RCSB PDB IDs: gH/gL/gO/PDGFRα (7LBF) [30], gH/gL/gO/TGFβR3 (7LBG) [30], gH/gL/UL128/UL130/UL31 (5VOB) [38], and gH/gL/UL128/UL130/UL31/NRP2 (7M22) [31].