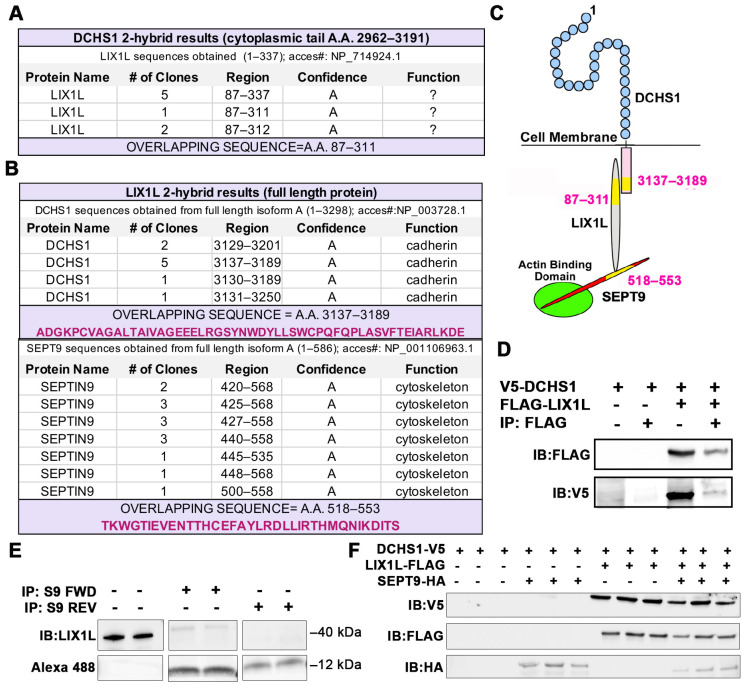
Figure 1.
Identification of DCHS1-LIX1L-SEPT9 (DLS) protein complex. (A) Yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) screen using cytoplasmic tail (A.A. 2962–3191) of Dachsous Cadherin Related-1 (DCHS1) as bait reveals Lix1-Like (LIX1L). (B) Y2H with full-length LIX1-Like (LIX1L) identifies DCHS1 and septin-9 (SEPT9) as binding partners. In A and B, confidence scores represent likelihood of an interaction, with A being the highest level of confidence (See Methods for details). (C) Diagram depicting interacting proteins and binding domains. (D) Co-Immunoprecipitation (co-IP) and immunoblotting (IB) analysis with DCHS1-V5 and LIX1L-FLAG transfected in HEK293T cells confirms protein interaction. (E) Co-IP and IB of cVIC protein lysate treated with 10 μg peptide mimicking the LIX1L-SEPT9 binding domain (S9-FWD:5-FAM-YGRKKRRQRRR-Ahx TKWGTIEVENTTHCEFAYLRDLLIRTHMQNIKDIT-Lys(Biotin), S9-REV:5-FAM-YGRKKRRQRRR-Ahx-TIDKINQMHTRILLDRLYAFECHTTNEVEITGWKT-Lys(Biotin)). (F) IB of DCHS1-V5, LIX1L-FLAG and SEPT9-HA co-transfected into HEK293T cells depicts stabilization of DCHS1 protein only in the presence of LIX1L.