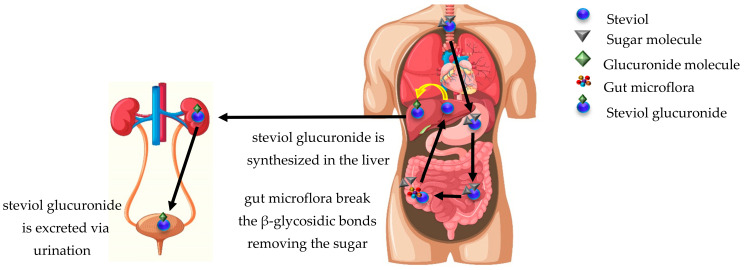
Figure 2.
SG metabolism in the human body. Steviol with sugar molecules attached to it enters the body, but it cannot be metabolized by the components of the upper GI track. SG metabolism starts in the large intestine, where gut microflora breaks the β-glycosidic bonds removing the sugar molecules, leaving the core steviol to be transported to the liver via the hepatic portal vein. In the liver, a glucuronide molecule is attached to steviol, leading to the formation of steviol glucuronide, which is subsequently transported to the kidneys via systemic circulation and is finally eliminated via urination. (The outline of the human body was reproduced from www.freepik.com, accessed on 20 December 2021).