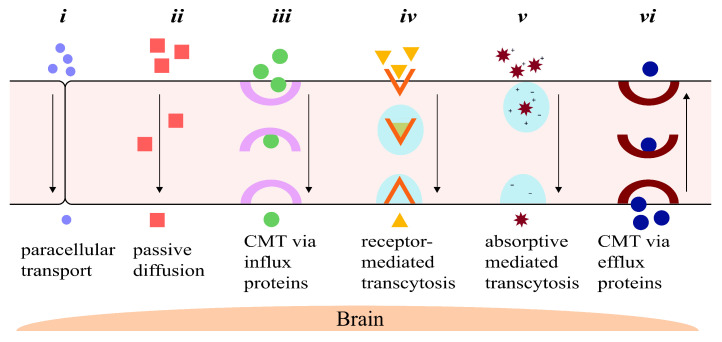
Figure 1.
A schematic representation of the six major ways drugs and other molecules travel across the blood–brain barrier: (i) paracellular transport between the tight junctions between the endothelial cells by small, hydrophilic molecules; (ii) passive diffusion through the endothelial cells of small lipophilic drugs; (iii) carrier-mediated transport of larger lipophilic molecules by influx carrier proteins; (iv) receptor-mediated transcytosis of larger molecules with affinity towards specific receptors; (v) absorptive-mediated transcytosis of large, cationic molecules by binding and ultimately absorbing into the luminal surface of the endothelial cell; and (vi) transport of unwanted molecules back into systemic circulation by efflux transporters.