Fig. 4 |. AMBRA1 acts as a tumour suppressor and its absence reduces sensitivity to inhibitors of CDK4/6 by promoting the formation of D-type cyclins–CDK2 complexes.
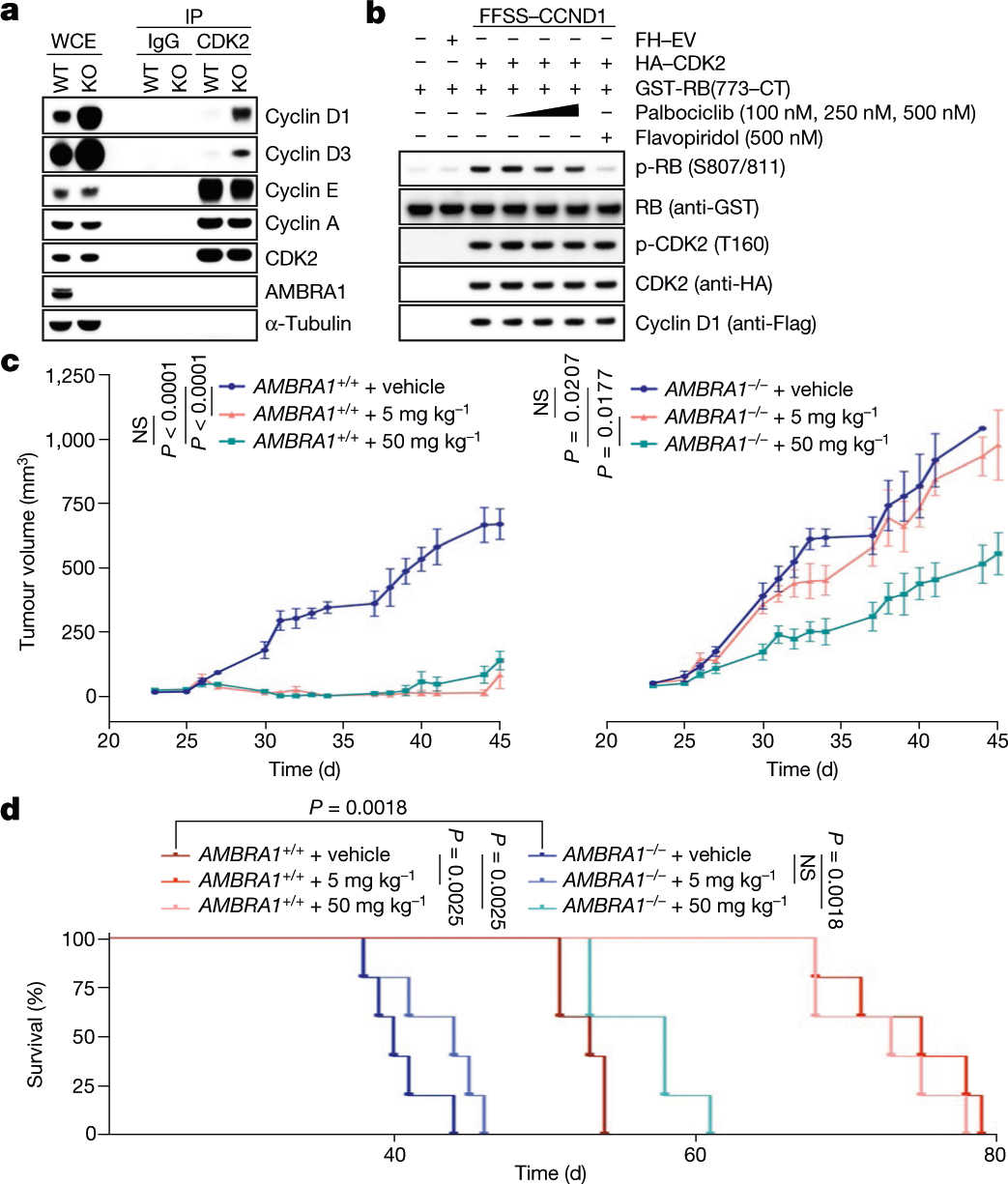
a, Endogenous CDK2 and IgG control immunoprecipitations (IPs) from parental and AMBRA1−/− HCT-116 cells. WCE, whole-cell extracts. b, HEK 293T cells were transfected as indicated. Immunopurified cyclin D1–CDK2 complexes were incubated with GST–RB(773-CT) and treated with palbociclib or flavopiridol. CT, C terminus. c, d, U-2932 cells expressing control short guide RNA (sgRNA) targeting luciferase or AMBRA1 were subcutaneously xenotransplanted in NSG mice and treated with PBS (vehicle) or palbociclib at the two indicated concentrations. c, Tumour volume. Data are mean ± s.e.m. (n = 5 per group at day 0). P values by unpaired, multiple-comparison t-test using the Holm–Sidak’s method, calculated at day 45 for the AMBRA1+/+ group and at day 40 for the AMBRA1−/− group (the latest time point where at least 3 mice per group were available). d, Survival curves. Experimental end point was declared when tumour volume reached 1,000 mm3 (n = 5 per group). P values by log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test. Unless otherwise noted, experiments were performed at least three independent times.
