Extended Data Fig. 5 |. Loss of AMBRA1 regulates D-type cyclins during normal cell cycle, upon nutrient deprivation and after genotoxic stress.
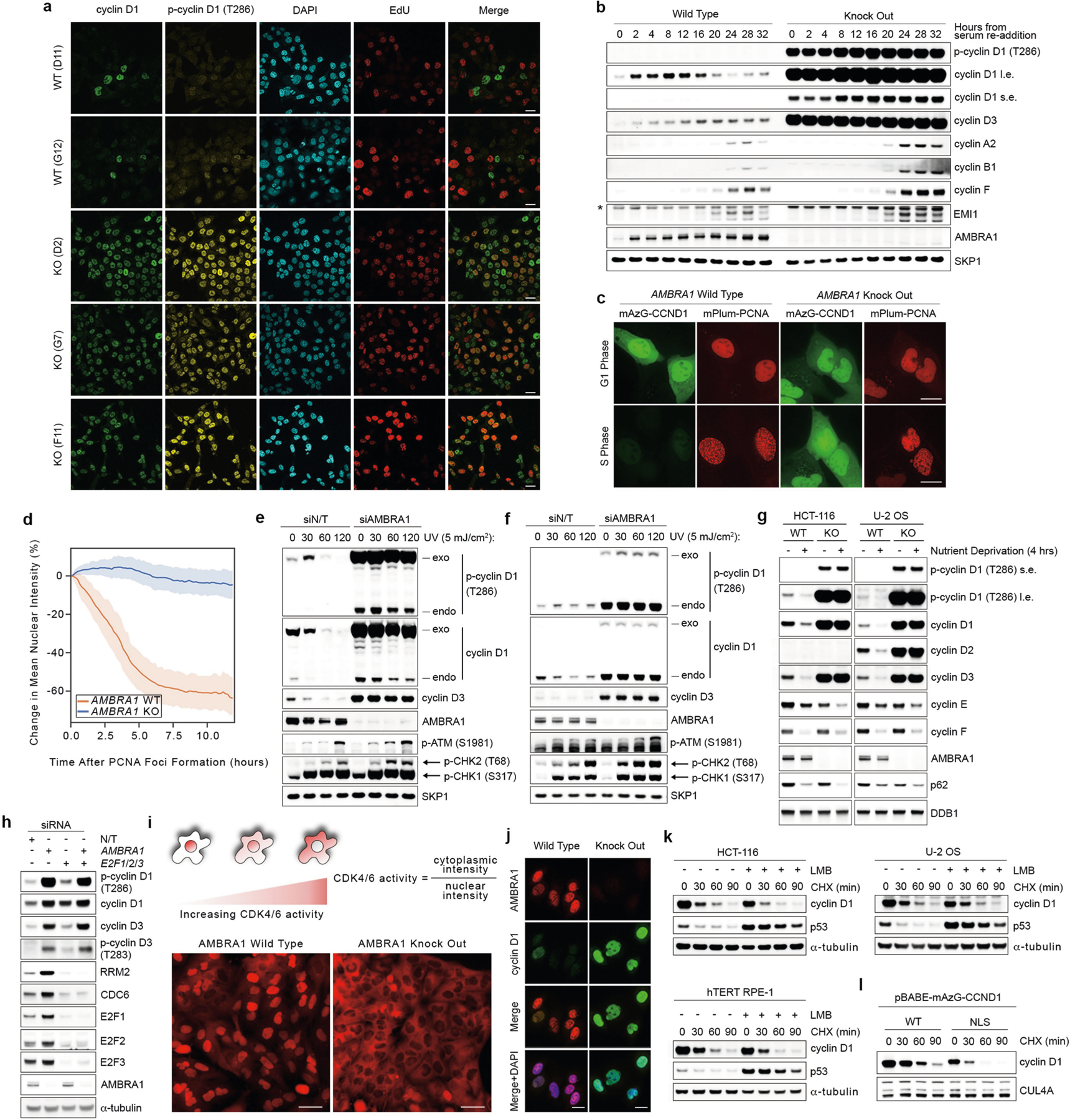
a, Three AMBRA1−/− and two AMBRA1+/+ clones were pulsed with EdU for 45 min before fixation with 4% paraformaldehyde, and immunofluorescent staining for the indicated proteins. Detection of EdU was accomplished using the Click-iT Plus EdU Alexa Fluor 647 Imaging Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). DAPI was used to detect DNA. Scale bars, 20 μm. b, AMBRA1+/+ and AMBRA1−/− T98G cells were serum-deprived for 72 h. Cells were then released with the re-addition of 10% FBS and collected at the indicated times. Cell extracts were immunoblotted as indicated. c, Representative images of AMBRA1+/+ and AMBRA1−/− U-2 OS cells stably infected with retroviruses expressing mAzG-CCND1 and mPlum-PCNA and monitored via live-cell imaging. Note that mPlum-PCNA forms nuclear foci during S phase. Scale bar, 20 μm. d, Quantification of mAzG-CCND1 changes in mean nuclear intensity in single cells tracked over time related to c. Plots represent percentage change from t = 0 (PCNA foci formation). Lines show mean and the shaded regions represent the 95% confidence interval. AMBRA1 WT, n = 12 cells; AMBRA1 KO, n = 34 cells. e, U-2 OS cells were infected with a retrovirus expressing mAzG-cyclin D1, and transfected with a non-targeting siRNA or an siRNA against AMBRA1 for two rounds. Cells were then exposed to UV (5 mJ cm−2) irradiation for the indicated times before collection. Cell extracts were immunoblotted as indicated. f, HCT-116 cells were infected with a retrovirus expressing mAzG-cyclin D1, and transfected with a non-targeting siRNA or an siRNA against AMBRA1 for two rounds. Cells were then exposed to UV (5 mJ cm−2) irradiation for the indicated times before collection. Cell extracts were immunoblotted as indicated. g, AMBRA1+/+ and AMBRA1−/− HCT-116 and U-2 OS cells were maintained in normal medium or nutrient-deprived in EBSS for 4 h before collection. Cell extracts were immunoblotted as indicated. h, HCT-116 cells were transfected with a non-targeting siRNA or combinations of siRNAs against AMBRA1, E2F1, E2F2 and E2F3 as indicated for three rounds before lysis and immunoblotting for the indicated proteins. i, T98G cells were transfected with an sgRNA control or an sgRNA targeting AMBRA1. AMBRA1−/− clones positive for gene editing were pooled together. Parental and AMBRA1−/− pooled T98G cells were then infected with a CDK4/6 activity reporter54 and seeded in glass-bottom plates. Three days after seeding, cells were stained with Hoechst 33342 before imaging. Scale bars, 50 μm. j, AMBRA1+/+ and AMBRA1−/− U-2 OS cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde and immunostained as indicated. DAPI was used to detect DNA. Scale bars, 20 μm. k, HCT-116, U-2 OS and hTERT RPE-1 cells were treated with leptomycin B (LMB) for 4 h before exposure to cycloheximide for the indicated times. Cell extracts were immunoblotted as indicated. l, U-2 OS cells were infected with retroviruses expressing either mAZG-tagged wild-type cyclin D1 or cyclin D1 fused to a nuclear localization signal (NLS). Cells were then treated with cycloheximide for the indicated times before collection. Cell extracts were immunoblotted as indicated. Unless otherwise noted, experiments were performed at least three independent times.
