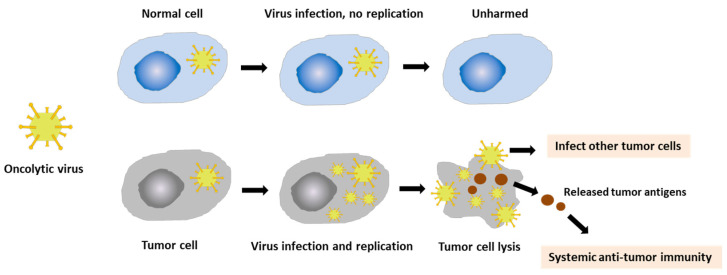
Figure 2.
Mechanism of action of oncolytic virus. After the oncolytic viruses (OVs) enter normal cells, the cells stimulate different signaling pathways to limit virus spread and promote rapid cell death and the viral clearance. The virus is not able to replicate in the normal cells, leaving them unharmed. In cancer cells, OVs replicate in and lyse the cancer cells, which can directly destroy tumor cells. In addition, the release of tumor antigens and other danger signals following cell death initiates a systemic anti-tumor immune response that promotes tumor regression at distant tumor sites that are not exposed to OVs.