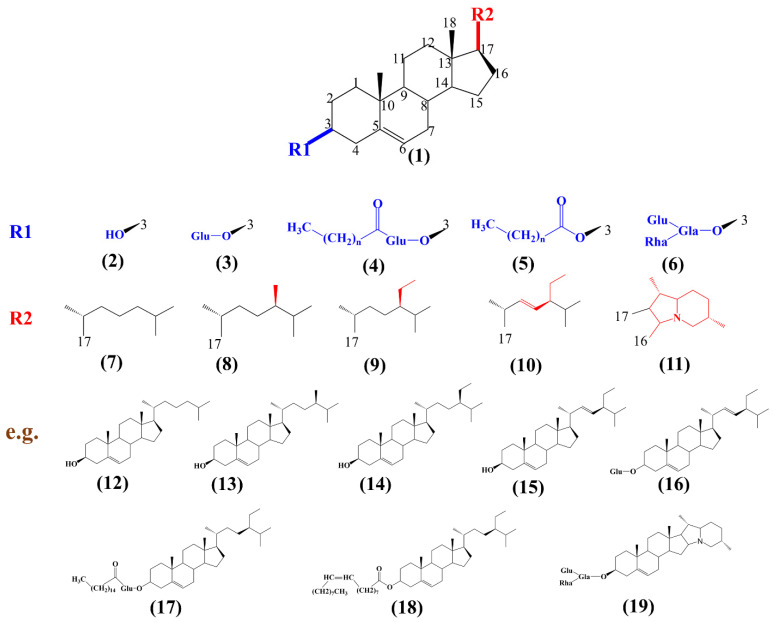
Figure 1.
The chemical structure of free sterols and conjugated sterol. R1 at C3 and R2 at C17 determine the diversity of sterols. (1) Tetracyclic skeleton of sterol; R1 determines the type of compound including, (2) free sterol, (3) steryl glucosides, (4) acylated steryl glucosides, (5) steryl esters, (6) steroidal glycoalkaloids. R2 determines the diversity of compounds. For example, the combination of (2) and (7) makes cholesterol (12), the combination of (2) and (8) makes campesterol (13), the combination of (2) and (9) makes β-sitosterol (14), the combination of (2) and (10) makes stigmasterol (15), the combination of (3) and (10) makes stigmasteryl glycose (16), the combination of (4) and (9) makes sitosteryl palmitoyl glucoside (17), the combination of (5) and (9) makes stigmasteryloleate (18), while the combination of (6) and (11) makes α-solanine (19). The differences in the R1 group and R2 group are shown in blue and red, respectively.