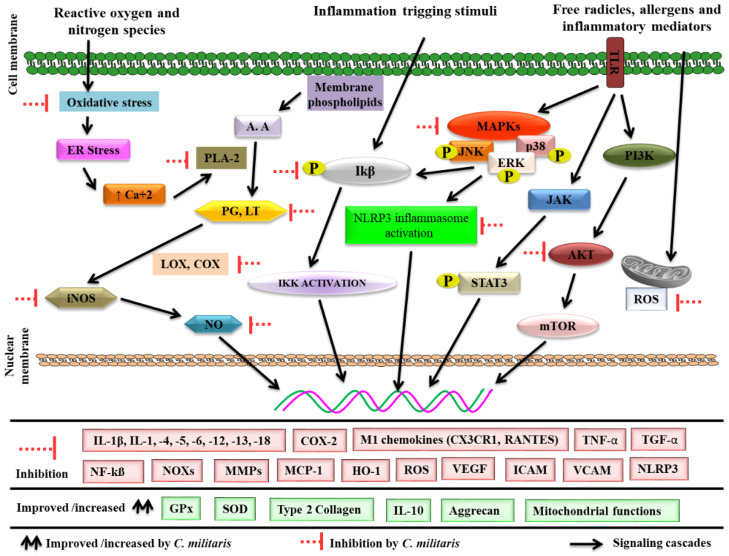
Figure 6.
C. militaris and its constituents associated anti-inflammatory molecular mechanisms. Arachidonic acid: A.A; Cyclooxygenase 2: COX-2; Heme oxygenase-1: HO-1; Interleukin-1β: (IL)-1β, -4, -5, -6, -10, -12, -13, -18; Intracellular adhesion molecule: ICAM; Inducible nitric oxide synthase: iNOS; Leukotrienes LT; Lipoxygenases: LOX; Monocyte chemotactic protein-1: MCP-1; Matrix metalloproteinases: MMPs; Nuclear factor-κB: NF-κB; phospholipase A2: PLA-2; Glutathione peroxidase: GPx; Prostaglandin: PG; Superoxide dismutase: SOD; Transforming growth factor-α: TGF-α; Tumor necrosis factor alpha: TNF-α; Vascular endothelial growth factor: VEGF; Vascular cell adhesion molecule: VCAM. Upward double arrow shows the improved/increased content or functionality. Single black arrow indicates signaling cascades, while the red symbol specifies the inhibition of inflammation associated signals and biomolecules.