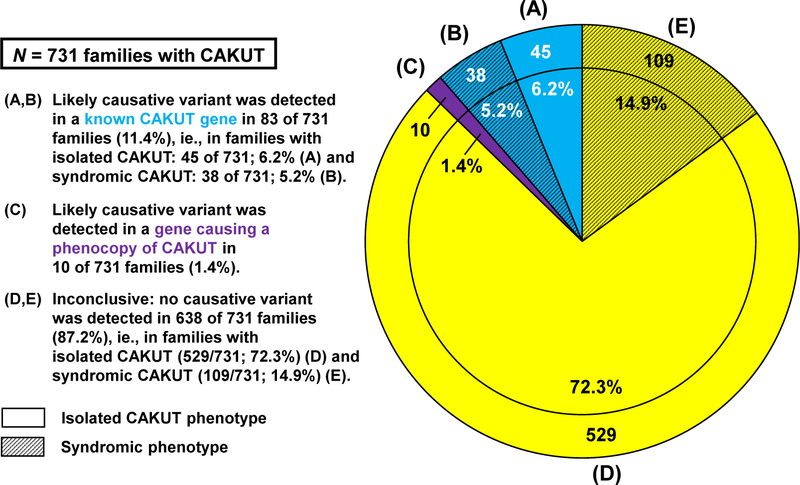
Figure 2. Results from exome sequencing evaluation of 731 families with CAKUT for likely causative variants in known CAKUT-causing genes and for phenocopies of CAKUT.
Exome sequencing (ES) data of 822 affected individuals with CAKUT from 731 unrelated families were analyzed for likely causative variants in the genes known to cause, if mutated, isolated CAKUT (23 genes, Supplemental Table 1), syndromic CAKUT (16 genes, Supplemental Table 2), and a syndrome with facultative CAKUT (135 genes, Supplemental Table 3) and for genes that represent a phenocopy of CAKUT (46 genes, Supplemental Table 4). The pie chart summarizes the findings for all 731 families, which is divided into the following subgroups. A. The clear blue segment denotes 45 of 731 (6.2%) families with isolated CAKUT, in which a likely causative variant in 1 of the genes known to cause CAKUT, if mutated, was detected. B. The hatched blue segment denotes 38 of 731 (5.2%) families with syndromic CAKUT, in which a likely causative variant in 1 of the genes known to cause CAKUT, if mutated, was detected. C. The purple segment denotes 10 of 731 (1.4%) families with CAKUT, in which a likely causative variant in a gene causing a phenocopy of CAKUT was detected. D. The clear yellow segment denotes 529 of 731 (72.3%) families with isolated CAKUT and inconclusive ES evaluation. E. The hatched yellow segment denotes 109 of 731 (14.9%) families with syndromic CAKUT and inconclusive ES evaluation. The outer ring segments denote the absolute number of families out of all 731 families with CAKUT; the inner circle segments show percentage of families from total (731 families = 100%). CAKUT, congenital anomalies of the kidneys and urinary tract.