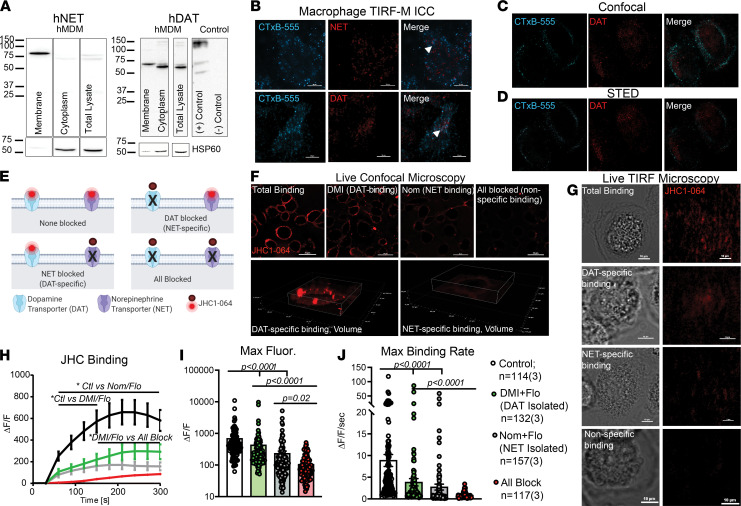
Figure 2. Human monocyte-derived macrophages express DAT and NET that are localized to the plasma membrane.
(A) Representative immunoblots for NET and DAT from macrophage intracellular and membrane fractions separated via biotinylation assay (splice sites indicated by solid lines). (B) Representative 40× total internal reflective fluorescence microscopy (TIRF-M) images of cultured macrophages labeled with CTxB-555 and either NET or DAT antibodies. CTxB-555 punctae appeared on the basal membrane, along with scattered punctae of NET (top) and DAT (bottom). Some punctae of CTxB colocalized with NET or DAT (arrowheads, n = 4 experiments). (C and D) Representative confocal images (C, n = 4 experiments) or stimulated emission depletion (STED) images (D, n = 2 experiments) on cultured human macrophages labeled with CTxB-555 and for DAT with some of the DAT signal colocalizing with the CTxB-555 signal at or near the membrane. (E) Schematic of the experimental design for JHC1-064 binding assay to identify NET-specific and DAT-specific binding. (F and G) Live-cell confocal (60×) and TIRF-M (40×) images of JHC1-064 binding to macrophages in conditions shown in E. (H) Quantifying the JHC1-064 signal from F shows that blocking NET or DAT decreased JHC1-064 binding. Blocking both transporters further decreased the JHC1-064 signal on macrophages (2-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons, P < 0.05). (I and J) The magnitude (I) and rate (J) of JHC1-064 binding to human macrophages were decreased by the addition of Nom or DMI. (I) Control versus DAT-specific (P < 0.0001), control versus NET-specific (P < 0.0001). (J) Control versus DAT-specific (P = 0.0004), control versus NET-specific (P < 0.0001). Blocking all 3 transporters further decreased the magnitude (I, P < 0.0001) and rate (J, P < 0.0001) of JHC1-064 binding. Images and data in F–J are from n = 114–157 cells/group from 3 independent experiments. Statistical analysis in I and J performed by Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s test for multiple comparisons.