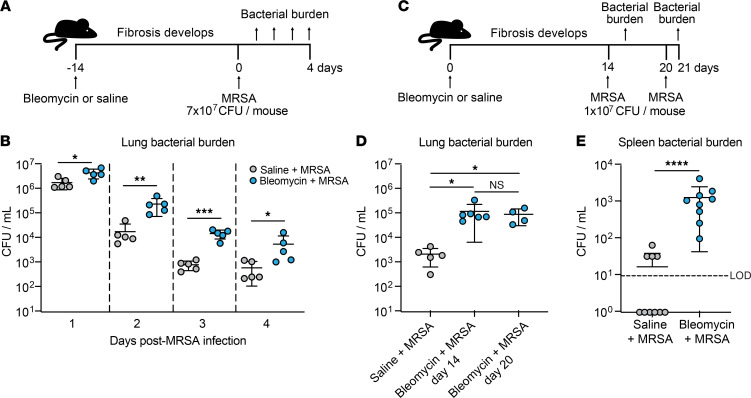
Figure 2. Fibrotic lung disease impairs MRSA clearance 14 and 21 days after bleomycin treatment.
(A) Mice were treated with bleomycin or saline 14 days prior to infection with MRSA (7 × 107 CFU/mouse). Lung bacterial burden was quantified 1–4 days after infection. (B) Lung bacterial burden from mice described in A. Bacterial burden was quantified at specified time points (n = 5 mice per group). Representative of 2 independent experiments. Data represent the means ± SD. Statistical analysis by multiple Student’s t tests. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (C) Mice were treated with saline or bleomycin and then infected with 1 × 107 CFU MRSA 14 or 20 days after bleomycin treatment. Lung bacterial burden was quantified 24 hours postinfection (day 15 or day 21). Saline-treated mice were infected on day 20 and MRSA was quantified on day 21. (D) Lung bacterial burden from mice described in C (saline + MRSA n = 5, bleomycin + MRSA day 14 n = 6, bleomycin + MRSA day 20 n = 4). Representative of 2 independent experiments. Data represent the means ± SD. Statistical analysis by Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons. *P < 0.05. (E) Spleen bacterial burden from mice infected with 1 × 107 CFU MRSA 20 days after bleomycin (n = 9) or saline (n = 10) treatment. CFU measured 24 hours postinfection. Data from 2 combined independent experiments. Data represent the means ± SD. Statistical analysis by Mann-Whitney U test. ****P < 0.0001. LOD, limit of detection.