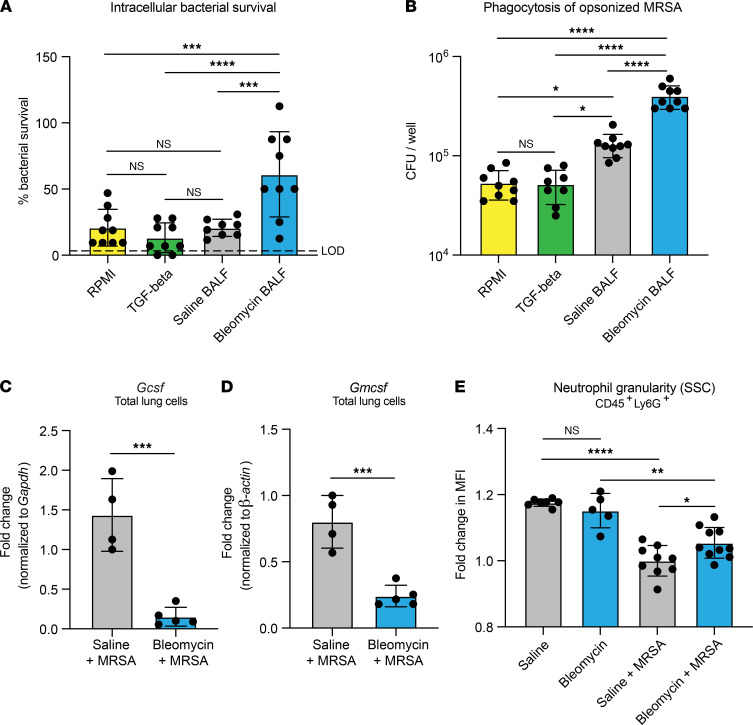
Figure 7. Soluble mediators in fibrotic lungs likely play a role in impaired effector function.
(A) Intracellular bacterial survival after uptake and killing of opsonized MRSA by bone marrow neutrophils from naive mice treated for 4 hours with complete RPMI, complete RPMI + TGF-β (2 ng/mL), or BALF from saline- or bleomycin-treated mice collected in complete RPMI. BALF was collected from mice 21 days after saline or bleomycin. Percentage survival is calculated by dividing the intracellular CFU quantified after 2 hours by the intracellular CFU quantified after 30 minutes and is representative of the bacterial killing by neutrophils. (B) Phagocytosis of opsonized MRSA by cells described in A. (A and B) Representative of 2 independent experiments; dots represent technical replicates of pooled cells (n = 9). Cells from 2 mice per group. Data represent the means ± SD. Statistical analysis by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. (C and D) Gcsf (C) and Gmcsf (D) measured via RT-qPCR of total lung cells isolated from mice treated with saline + MRSA (n = 4) or bleomycin + MRSA (n = 5). Representative of 2 independent experiments. Data represent the means ± SD. Statistical analysis by unpaired Student’s t test. ***P < 0.001. (E) Neutrophil granularity as measured by mean fluorescence intensity of cellular side-scatter (SSC). Neutrophils were analyzed 21 days after treatment with saline (n = 7), bleomycin (n = 5), saline + MRSA (n = 9), or bleomycin + MRSA (n = 10). Mice were infected with MRSA 24 hours before analysis. Data from 2 combined experiments. Data represent the means ± SD. Statistical analysis by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001.