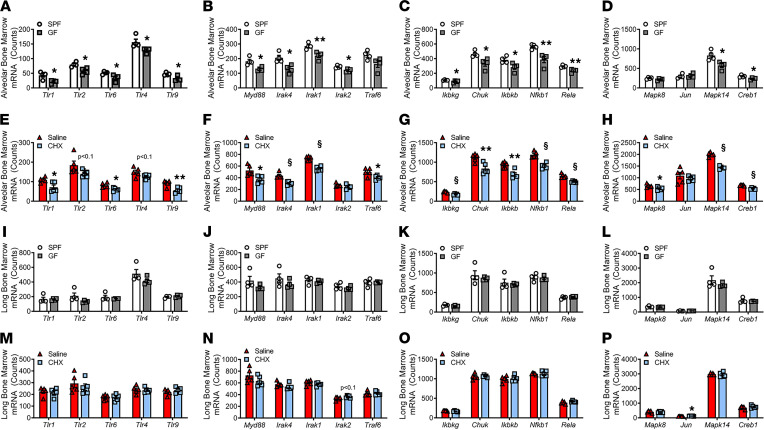
Figure 5. Commensal oral microbiota has immunostimulatory actions distinct from the systemic microbiota, which substantially upregulates TLR signaling in alveolar BM.
(A–D) nCounter analysis was utilized to determine the expression of TLRs and related downstream signaling molecules in the alveolar BM (ABM) of SPF versus GF mice; n = 4/gp. (A) TLR expression. (B) MyD88-dependent adaptor molecule expression. (C) NF‑κB signaling factor expression. (D) MAPK signaling factor expression. (E–H) nCounter analysis of TLRs and related downstream signaling molecules in the ABM of saline versus CHX mice; n = 6/gp. (E) TLR expression. (F) MyD88-dependent adaptor molecule expression. (G) NF‑κB signaling factor expression. (H) MAPK signaling factor expression. (I–L) nCounter analysis of TLRs and related downstream signaling molecules in the long BM (LBM) of SPF versus GF mice; n = 4/gp. (I) TLR expression. (J) MyD88-dependent adaptor molecule expression. (K) NF‑κB signaling factor expression. (L) MAPK signaling factor expression. (M–P) nCounter analysis TLRs and related downstream signaling molecules in the LBM of saline versus CHX mice; n = 6/gp. (M) TLR expression. (N) MyD88-dependent adaptor molecule expression. (O) NF‑κB signaling factor expression. (P) MAPK signaling factor expression. Unpaired t test; data presented as mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, §P < 0.001.