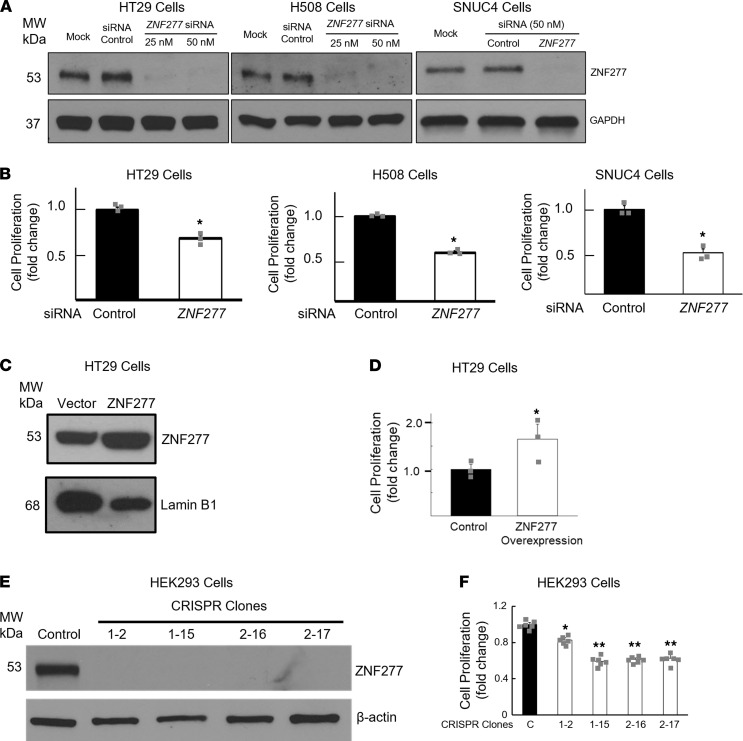
Figure 4. ZNF277 promotes human colon cancer cell proliferation.
(A) ZNF277 RNA interference reduces ZNF277 protein expression in human colon cancer cells. Immunoblots of extracts from HT29, H508, and SNUC4 human colon cancer cells after ZNF277 knockdown with the indicated concentrations of ZNF277 siRNA and 50 nM mock siRNA. (B) ZNF277 deficiency attenuates human colon cancer cell proliferation. Cells were transfected for 24 hours with siRNA, and cell proliferation was measured after an additional 24-hour incubation. *P < 0.05 versus control siRNA. Data represent mean ± SEM from 3 separate experiments. (C) Immunoblotting confirms ZNF277 overexpression in HT29 cells transfected with plasmid containing full-length human ZNF277 cDNA. (D) Overexpressing ZNF277 stimulates HT29 cell proliferation. *P < 0.05 versus control cells. Data represent mean ± SEM from 3 separate experiments. (E) Immunoblots reveal lack of ZNF277 expression in 4 HEK293 lines following CRISPR KO of ZNF277. (F) CRISPR KO of ZNF277 attenuates HEK293 cell proliferation. *P < 0.05 versus control cells. **P < 0.05 versus line 1-2. Data are shown as mean ± SD from 7 separate experiments. Data were analyzed using 2-tailed t tests and 1-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test. β-Actin and lamin B1 were used as loading controls in A and C, respectively.