Figure 6. Schematic drawing of the fractal branching microchannel net chip.
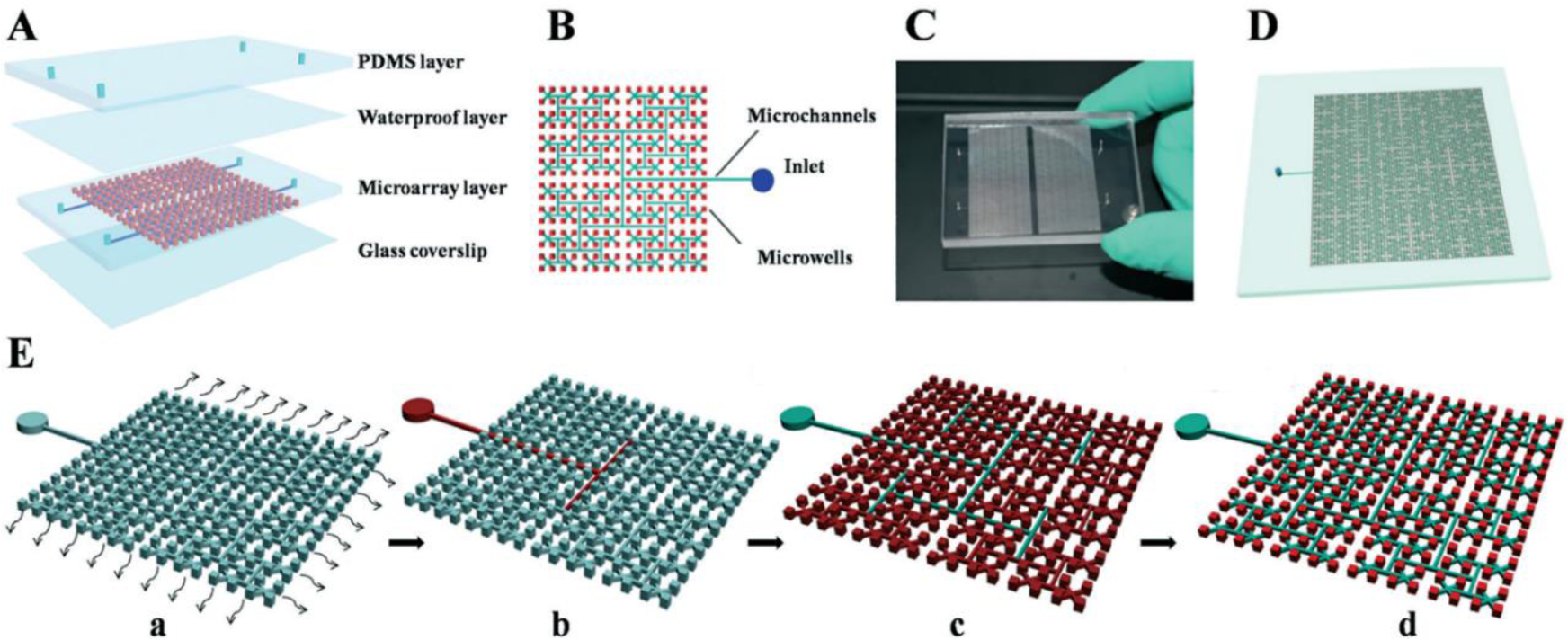
(Zhu et al., 2017). (A) Schematic diagram of the chip that has 4096 microwells for dPCR reaction. (B) Diagram of the details of the chip design. (C) Photograph of the chip. (D) The scalability of the chip with 16384 microwells in each reaction panel. (E) The principle and operation procedure of the microfluidic device: (a) the chip is degassed in a vacuum pump and then adhesive tape is attached to seal the top surface of the chip after the degassing step; (b) the adhesive tape is punctured, and the reagent can be dispensed into the inlet, while the degassing-drive flow primes the sample into the microwells quickly; (c) the oil is then dispensed into the inlet, and the oil phase is self-primed into the channels; (d) all the sample solutions are partitioned into each microwell by the oil, and no sample is wasted. Finally, the chip is sealed using a coverslip to run PCR amplification. Adapted from Ref. 113 with permission from the Royal Society of Chemistry.
