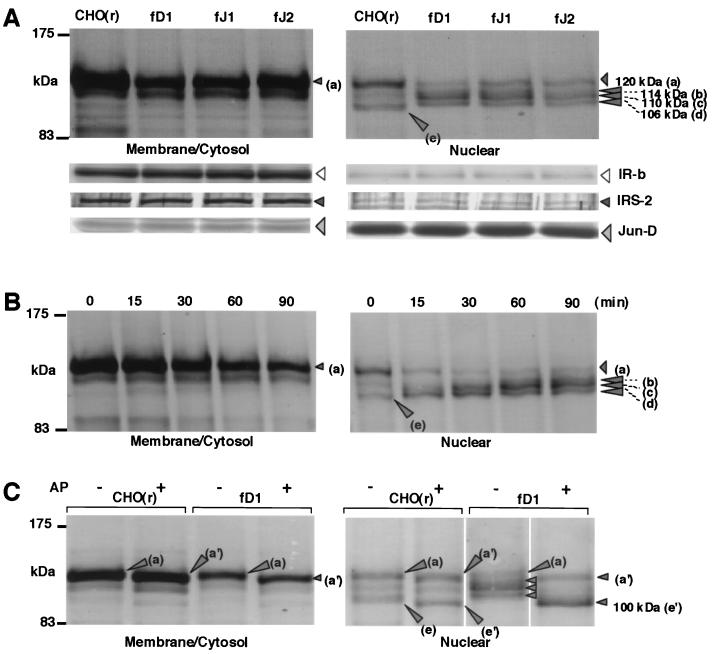
FIG. 5.
Induction of cleavage, hyperphosphorylation, and nuclear accumulation of the intracellular domain of Notch2 by DSL proteins. (A) Cleavage of the membrane-spanning subunit of Notch2 and nuclear accumulation of intracellular domain of Notch2 by stimulation with various full-length DSL proteins. BaF3 cells were collected 1.5 h after coculture with CHO(r) lines stably expressing or not expressing various exogenous full-length DSL proteins. MC and N fractions were prepared as described in Materials and Methods, and in each fraction Notch2 fragments containing an intracellular domain were analyzed by Western blot using an anti-Notch2 antibody after immunoprecipitation. As controls for correct fractionation of the MC and N fractions, antibodies against IRβ for membrane proteins, insulin receptor substrate-2 (IRS-2) for cytosolic proteins, and Jun-D for nuclear proteins were used for each fraction in Western blot analysis. (B) Time-course analysis of Notch2 after stimulation with fD1-CHO. (C) Effect on Notch2 fragments of alkaline phosphatase (AP) treatment. From each MC and N fraction prepared from BaF3 after coculture with wild-type CHO(r) and fD1-CHO, Notch2 fragments containing the intracellular domain were immunoprecipitated. The samples were then treated by alkaline phosphatase and subjected to Western blotting.