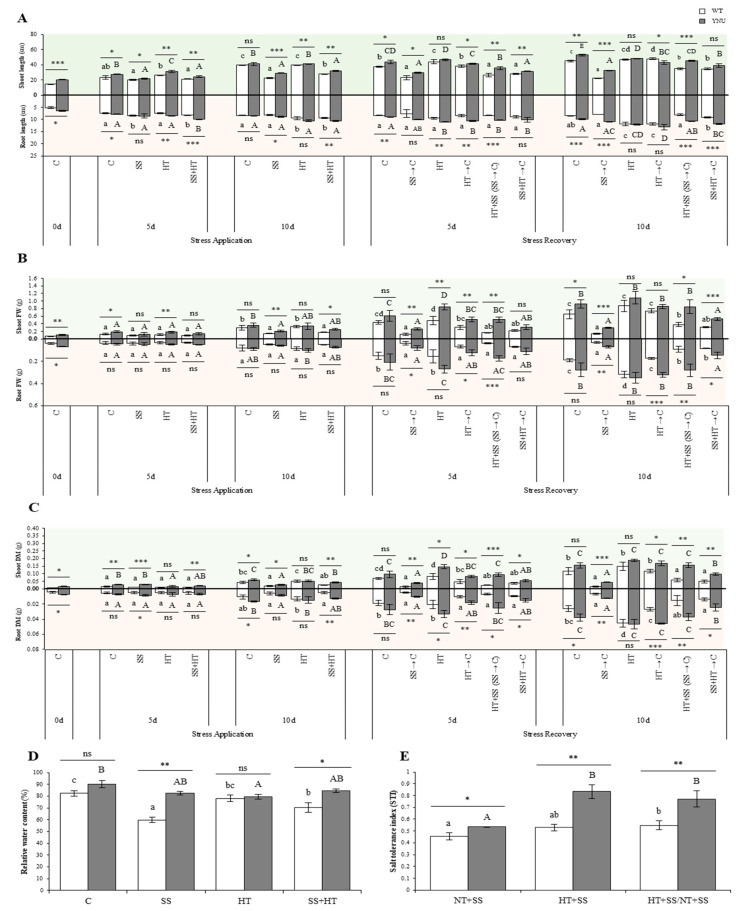
Figure 1.
Morphological responses to salinity (SS), high-temperature (HT), and combined salinity and heat (SS + HT) of ‘Yukinkomai’ (WT) and ‘YNU31-2-4’ (YNU) rice seedlings; (A) Shoot (top panel) and root (lower panel) lengths, (B) shoot (top panel) and root (lower panel) fresh weight (FW), (C) shoot (top panel) and root (lower panel) dry matter (DM), (D) relative water content (RWT), and (E) salt tolerance index (STI) of WT and YNU plants under control normal-temperature (NT) (C: 26/23 °C, 0 mM NaCl), salt stress (SS: 26/23 °C, 75 mM NaCl), high-temperature (HT: 30/26 °C, 0 mM NaCl), combined stress (SS + HT: 30/26 °C, 75 mM NaCl), and stress-release (recovery) conditions. Bars = 10 cm. Values represent the means ± SE determined from three independent experiments using 4 plants in each experiment. Means within the same graph followed by different lowercase (WT) and uppercase (YNU) letters are significantly different at p < 0.05 according to the Tukey’s HSD test. Asterisks represent statistical significance of difference using Student’s t-statistic with *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05, ns: non-significant.