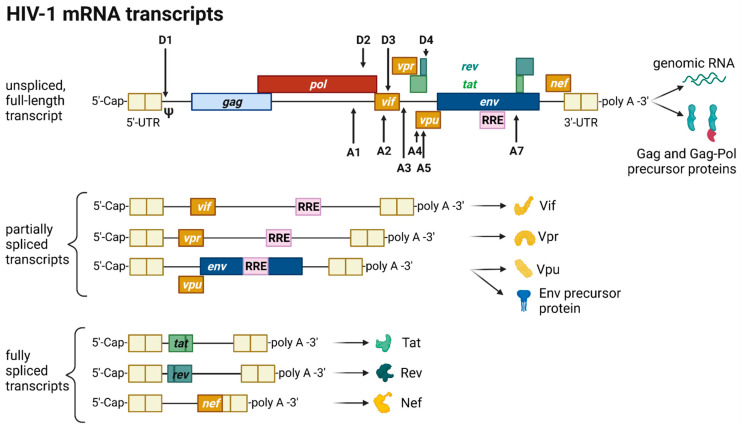
Figure 3.
HIV-1 mRNA transcripts and splice sites. HIV-1 transcripts are categorized into three classes: unspliced, full-length genomic gRNA (~9 kb), partially spliced, intron-containing mRNAs (~4 kb) and fully spliced, intronless mRNAs (~2 kb). The class of unspliced mRNAs serves either as gRNA later encapsidated into a virion or as a template for the synthesis of Gag and Gag-Pol precursor proteins. Splicing at splice donor sites (D) to splice acceptor sites (A) generates either partially or fully spliced transcripts depending on the splice sites utilized. All processed HIV mRNAs are spliced at the major splice donor site D1 to a downstream splice acceptor, removing the packaging signal Ψ. In fully spliced mRNAs, the Rev-responsive element (RRE)-containing intron flanked by D4 and A7 is spliced out. The viral proteins Tat, Rev, and Nef are translated from fully spliced mRNAs, whereas Vif, Vpr, Vpu, and the Env precursor protein gp160 are translated from partially spliced transcripts harboring the RRE structure. All transcripts are flanked by untranslated regions (UTR) at the 5′- and 3′-end.