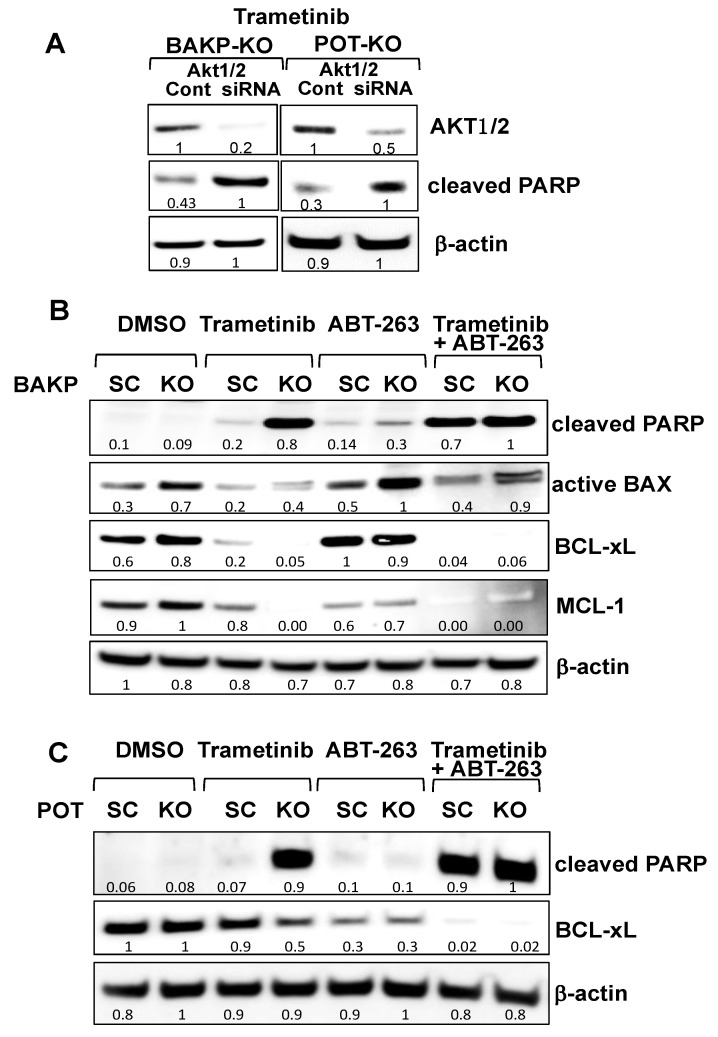
Figure 7.
siRNA knockdown of AKT1/2 in BAKP (A, left panel) and POT cells (A, right panel), or BCL-2 family inhibitor ABT-263 and/or CD133 knockdown reveals that AKT1/2 siRNA knockdown or BCL-2 family inhibition with ABT-263 plus CD133 knockdown both block the AKT pathway, inducing maximum apoptosis in the presence of trametinib in BAKP (B) and POT cells (C). (A) BAKP-KO and POT-KO cells were transfected with AKT1/2 siRNA pool or the scrambled control siRNA (“Cont”). Then, 48 h after transfection, cells were treated with 100 mM trametinib for 24 h, and subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies to AKT1, cleaved PARP, or β-actin. (B) BAKP-KO and (C) POT-KO cells or their respective controls BAKP-SC and POT-SC cells were treated for 48 h with trametinib (100 nM) or the BCL-2 family inhibitor ABT-263 (100 nM) alone or in combination, and then subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies to cleaved PARP, active BAX, BCL-xL, MCL-1, or β-actin. Densitometric analysis comparing intensities of protein bands relative to bands with the highest intensity is shown in immunoblots.